美国宾夕法尼亚大学Michela Locci小组的最新研究揭示了mRNA疫苗的不同组分合作指导有效的生发中心反应。2025年12月16日出版的《细胞》杂志发表了这项成果。
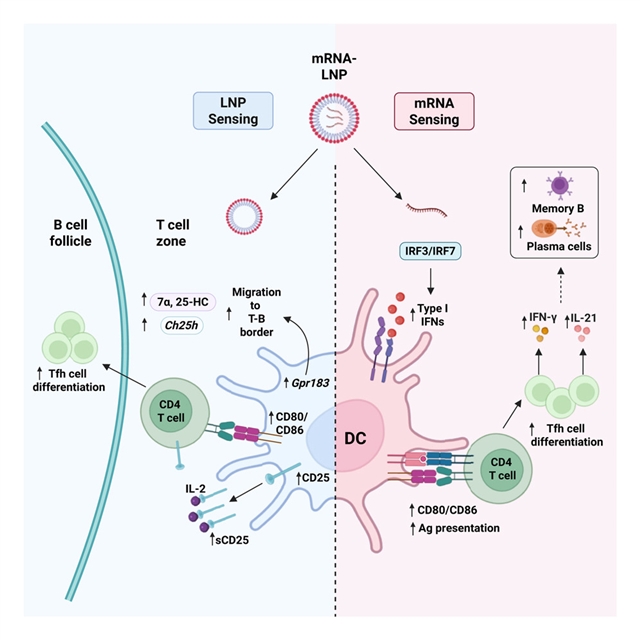
在此,该课题组研究人员反卷积LNPs和mRNA诱导的信号,这些信号指示树突状细胞(DCs)促进Tfh细胞分化。小组证明mRNA驱动I型干扰素的产生,这种干扰素作用于DCs以促进其成熟和Tfh细胞分化,并有利于浆细胞和记忆B细胞的反应。与此同时,LNPs允许引流淋巴结内的DCs摄取mRNA,也通过塑造CD25+ DCs的定位来调节Tfh细胞的反应。他们的工作揭示了诱导Tfh细胞所需的mRNA和LNPs的独特佐剂特征,这对合理的疫苗设计具有重要意义。
研究人员表示,核苷修饰信使RNA (mRNA)疫苗通过其促进T滤泡辅助细胞(Tfh)分化的能力引发保护性抗体。mRNA疫苗的脂质纳米颗粒(LNPs)具有固有的佐剂活性。然而,核苷修饰的mRNA在多大程度上被感知并有助于Tfh细胞反应仍未确定。
附:英文原文
Title: Distinct components of mRNA vaccines cooperate to instruct efficient germinal center responses
Author: Diana Castao, Emily Bettini, Binod Kumar, Aleksey Chudnovskiy, Anna Siv, Giulia Protti, Sandra Nakadakari-Higa, Simona Ceglia, Nina De Luna, Joy E. Chiu, Katlyn Lederer, Shuk Hang Li, Hassaan Ibrahim, Hiromi Muramatsu, Thandiswa Mdluli, Edit Abraham, Sinem E. Sahingur, Ivan Maillard, Ying K. Tam, Sunny Shin, Scott E. Hensley, Jonathan J. Miner, Zoltan Lipinszki, Andrea Reboldi, Norbert Pardi, Roberto Spreafico, Gabriel D. Victora, Michela Locci
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-16
Abstract: Nucleoside-modified messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines elicit protective antibodies through their ability to promote T follicular helper (Tfh) cell differentiation. The lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) of mRNA vaccines possess inherent adjuvant activity. However, the extent to which the nucleoside-modified mRNA is sensed and contributes to Tfh cell responses remains undefined. Herein, we deconvolute the signals induced by LNPs and mRNA that instruct dendritic cells (DCs) to promote Tfh cell differentiation. We demonstrate that the mRNA drives the production of type I interferons, which act on DCs to enhance their maturation and Tfh cell differentiation, and favors plasma cells and memory B cell responses. In parallel, LNPs, which allow for mRNA uptake by DCs within the draining lymph node, also modulate Tfh cell responses by shaping the localization of CD25+ DCs. Our work unravels distinct adjuvant features of mRNA and LNPs necessary for the induction of Tfh cells, with implications for rational vaccine design.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.11.023
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell/abstract/S0092-8674(25)01358-3
