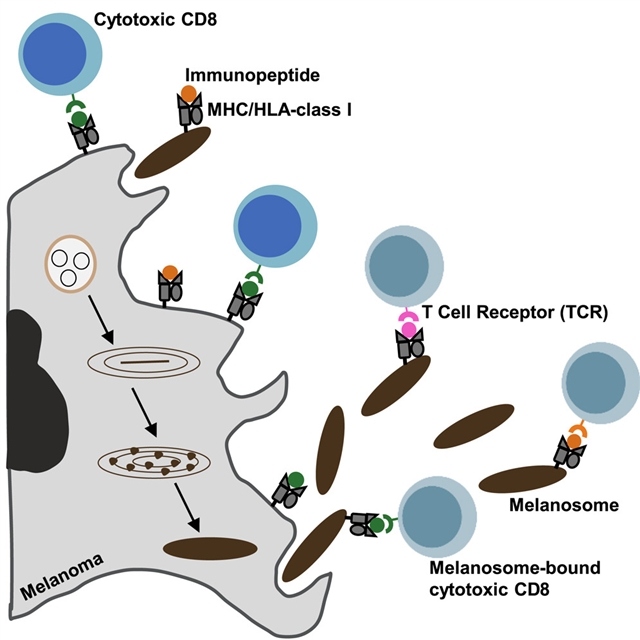
特拉维夫大学Shivang Parikh团队的一项最新研究显示,黑色素瘤细胞通过分泌HLA诱骗细胞毒性T细胞以促进免疫逃逸。相关论文于2025年12月15日发表于国际顶尖学术期刊《细胞》杂志上。
研究组发现黑色素瘤细胞分泌的大细胞外囊泡(称为黑素体)被主要组织相容性复合体(MHC)分子修饰,这些分子通过T细胞受体(TCR)刺激CD8+ T细胞,引导T细胞功能障碍和凋亡。免疫肽组学和T细胞受体测序(TCR-seq)分析显示,这些黑素小体携带MHC结合的肿瘤相关抗原,具有更高的亲和力和免疫原性,它们与肿瘤细胞竞争,直接与TCR-MHC相互作用。对黑色素瘤患者的活检分析证实,黑素小体可以诱捕浸润淋巴细胞,诱导部分活化,并降低CD8+ T细胞的细胞毒性。体内抑制黑素小体分泌可显著降低肿瘤免疫逃逸。这些发现表明MHC输出保护黑色素瘤免受T细胞的细胞毒性作用。他们的研究强调了一种新的免疫逃避机制,并提出了一种增强肿瘤免疫的治疗途径。
据介绍,虽然黑色素瘤细胞经常表达大量突变蛋白,但反应性T细胞的浸润很少导致肿瘤根除免疫。
附:英文原文
Title: HLA export by melanoma cells decoys cytotoxic T cells to promote immune evasion
Author: Yoav Chemla, Orit Itzhaki, Stav Melamed, Chen Weller, Yuval Sade, Paulee Manich, Keren Reshef, Nicolas Xenidis, Avishai Maliah, Gilad Levy, Roma Parikh, Osnat Bartok, Opal Levy, Itay Tal, Gal Aziel, Abraham Nissani, Sharon Yunger, Daniela Likonen, Vitaly Kliminsky, Tamar Golan, Coralie Capron, Valentina Ace, Ronen Levy, Diana Rasoulouniriana, Zohar Eyal, Yuval Barzilay, Roi Balaban, Aseel Khateeb, Rami Khosravi, Amir Grau, Tamar Ziv, Polina Greenberg, Dvir Netanely, Hananya Vaknin, Xunwei Wu, Yael Amitay, Ronen Brenner, Julia María Martínez Gómez, Dov Hershkovitz, Tal Yardeni, Valentina Zemser-Werner, Oren Kobiler, Yael Friedmann, David Bassan, Ron Shamir, Lea Eisenbach, Nadine Santana-Magal, Michael Milyavsky, Galit Eisenberg, Leeat Keren, Merav Cohen, Dvir Gur, Boaz Barak, Michal Lotem, David Sprinzak, Shoshana Greenberger, David Fisher, Michal J. Besser, Mehdi Khaled, Pierre Close, Ronnie Shapira, Sebastien Apcher, Asaf Madi, Mitchell P. Levesque, Francessca Rapino, Yaron Carmi, Shivang Parikh
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-15
Abstract: While melanoma cells often express a high burden of mutated proteins, the infiltration of reactive T cells rarely results in tumor-eradicating immunity. We discovered that large extracellular vesicles, known as melanosomes, secreted by melanoma cells are decorated with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules that stimulate CD8+ T cells through their T cell receptor (TCR), causing T cell dysfunction and apoptosis. Immunopeptidomic and T cell receptor sequencing (TCR-seq) analyses revealed that these melanosomes carry MHC-bound tumor-associated antigens with higher affinity and immunogenicity, which compete with their tumor cell of origin for direct TCR-MHC interactions. Analysis of biopsies from melanoma patients confirmed that melanosomes trap infiltrating lymphocytes, induce partial activation, and decrease CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity. Inhibition of melanosome secretion in vivo significantly reduced tumor immune evasion. These findings suggest that MHC export protects melanoma from the cytotoxic effects of T cells. Our study highlights a novel immune evasion mechanism and proposes a therapeutic avenue to enhance tumor immunity.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.11.020
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell/abstract/S0092-8674(25)01316-9
