近日,德国亚琛大学Patricia Martínez-Garzón团队报道了马尔马拉主断层向伊斯坦布尔方向的渐进东断裂。2025年12月11日出版的《科学》杂志发表了这项成果。
土耳其西北部的马尔马拉主断层是欧洲范围内地震风险最高的区域。2025年发生的MW6.2级地震是该断层带60余年来最强烈的地震。
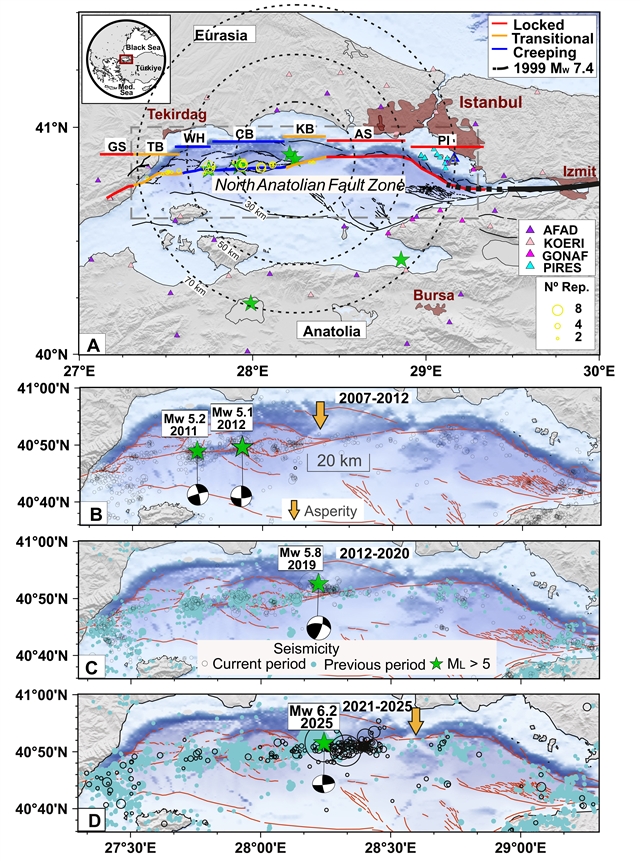
研究组整合了多时间尺度的观测数据,包括十年来MW>5级地震的演变过程、破裂动力学特征及余震分布模式。研究表明,过去约15年间该断层带发生了一系列向东扩展的MW>5级地震事件,并呈现出逐渐向东部分破裂的趋势。当前断层的地震活跃段包含蠕滑段和过渡段,其中最新震群活动位于伊斯坦布尔以南可能处于闭锁状态的王子群岛段附近——该段具备发生MW~7级地震的潜力。该分析强调了对马尔马拉主断层该区域实施实时监测的必要性。
附:英文原文
Title: Progressive eastward rupture of the Main Marmara fault toward Istanbul
Author: Patricia Martínez-Garzón, Xiang Chen, Dirk Becker, Sebastián Núez-Jara, Recai Feyiz Kartal, Elif Türker, Georg Dresen, Yehuda Ben-Zion, Jorge Jara, Fabrice Cotton, Filiz Tuba Kadirioglu, Tubay Kili, Marco Bohnhoff
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-11
Abstract: The Main Marmara fault (MMF) in northwestern Türkiye poses the highest seismic risk in broader Europe. The 2025 MW 6.2 was the largest earthquake along the MMF in >60 years. We integrated observations from multiple temporal scales including the decade-long evolution of M > 5 earthquakes, their rupture dynamics and aftershock patterns. We show a series of eastward propagating M>5 events and a gradual eastward partial rupture of the MMF over the last ~15 years. The seismically active portion of the fault includes creeping and transitional segments with some of the most recent seismicity located near the presumably locked Princes Islands segment south of Istanbul that has the potential to generate a M~7 earthquake. Our analysis highlights the necessity of real-time monitoring of this part of the MMF.
DOI: adz0072
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adz0072
