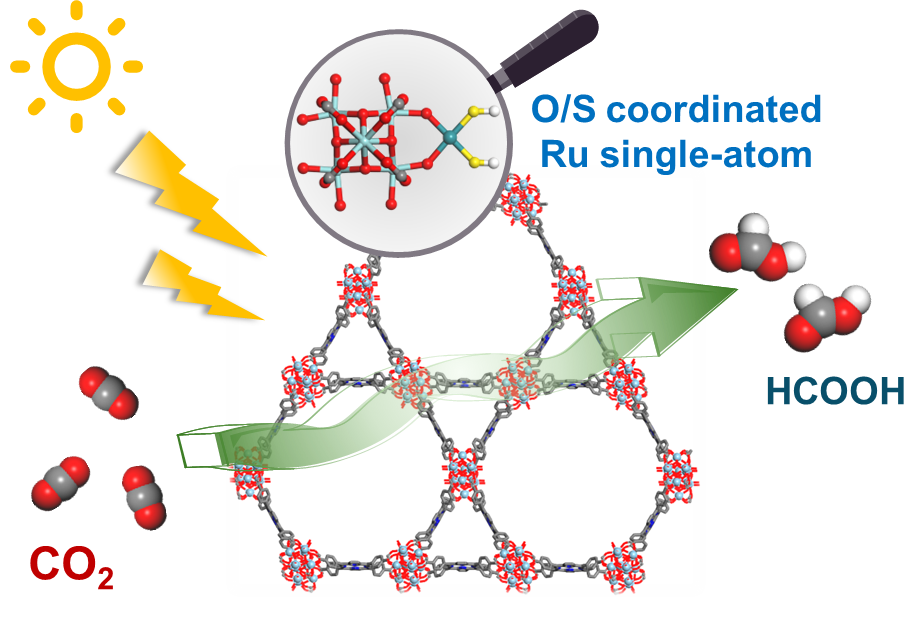
近日,中山大学张利团队研究了用于CO2光还原的卟啉金属-有机框架中的S配位Ru单原子工程。该项研究成果发表在2025年12月11日出版的《结构化学》杂志上。
在CO2光还原反应中,单原子催化剂的性能可通过精确调控其配位结构进行优化。
研究组通过在固定于卟啉基金属有机框架(Zn-PCN-222)Zr6O8簇上的钌单原子(Ru-SAs)中引入巯基(–SH)进行修饰。所得材料RuS-SAs@Zn-PCN-222在以氨硼烷为H*供体、将CO2还原为HCOO−的光催化反应中表现出高活性,其HCOO−生成速率达54.4 mmol·g–1·h–1,选择性为99.9%。该速率分别是Zn-PCN-222和未修饰巯基的Ru-SAs@Zn-PCN-222的约20.1倍和4.5倍。
光电化学测试表明,引入的RuS-SAs增强了RuS-SAs@Zn-PCN-222中光生电荷的分离和迁移。进一步的原位实验揭示,RuS-SAs既可接收来自Zn-PCN-222的光生电子,也能接受来自–SH基团的电子,随后将其注入惰性CO2分子中,从而促进CO2活化及其与H*的后续偶联形成HCOO−。
附:英文原文
Title: Engineering S-coordinated Ru single-atoms in a porphyrinic metal-organic framework for CO2 photoreduction
Author: anonymous
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-11
Abstract: The catalytic performance of single-atom catalysts in CO2 photoreduction can be optimized through precise modulation of the coordination structures of single-atoms. In this study, Ru single-atoms (Ru-SAs) immobilized on the Zr6O8 clusters of a porphyrinic metal–organic framework (Zn-PCN-222) were modified with sulfhydryl groups (–SH). The resulting RuS-SAs@Zn-PCN-222 exhibited high photocatalytic activity for CO2 reduction to HCOO using ammonia borane as the H* donor, giving rise to a HCOO production rate of 54.4 mmol·g–1·h–1 with 99.9% selectivity, which was approximately 20.1 and 4.5 times higher than that of Zn-PCN-222 and –SH-free Ru-SAs@Zn-PCN-222, respectively. Photoelectrochemical measurements demonstrated that the incorporated RuS-SAs enhanced the separation and migration of photogenerated charges in RuS-SAs@Zn-PCN-222. Further in situ experiments revealed that the RuS-SAs could accept photogenerated electrons from Zn-PCN-222 as well as electrons from the –SH groups, and then inject to inert CO2 molecules, thereby facilitating CO2 activation and its subsequent coupling with H* to form HCOO.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100841
Source: https://cjsc.ac.cn/cms/issues/941
Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry:《结构化学》,创刊于1982年。隶属于中国结构化学杂志,最新IF:2.2
官方网址:http://cjsc.ac.cn/
投稿链接:https://www2.cloud.editorialmanager.com/cjschem/default2.aspx
