近日,中国科学院大连化物所汪国雄团队报道了面向强化CO2电热催化甲烷干重整的原位溶出高密度镍纳米颗粒的LaAl0.3Mn0.2Ni0.5O3−δ阴极。这一研究成果发表在2025年12月11日出版的《美国化学会志》上。
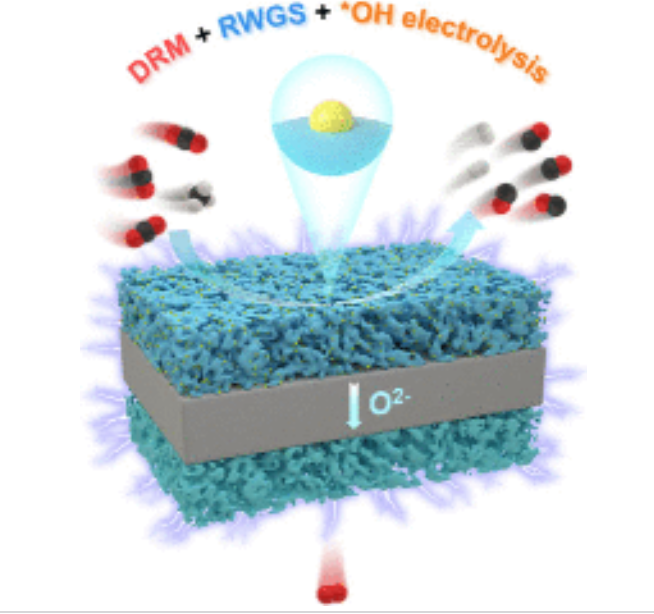
串联电热催化系统将甲烷干重整、逆水煤气变换及水电解反应集成于固体氧化物电解池内,为富二氧化碳原料的利用开辟了新途径。然而,界面特性与催化活性及稳定性之间的关联机制仍是重大挑战。
研究组通过调控铝和锰的共掺杂策略,重点关注在LaAl0.3Mn0.2Ni0.5O3−δ阴极上溶出高密度、分散良好且半嵌入结构的纳米颗粒。这些丰富且稳定的金属@钙钛矿界面位点对串联电热催化系统表现出高本征活性:在800°C下处理多种富二氧化碳原料(CO2/CH4 = 2–4)时,体系实现了超过92%的单程CO2与CH4转化率、超过93%的合成气产率、高达3.91的表观CH4还原度,以及73.77 molCH4 molNi–1 s–1的CH4周转频率。
原位电化学漫反射红外傅里叶变换光谱与密度泛函理论计算共同揭示了*OH电解在串联催化过程中的关键作用。该工作阐明了串联电热催化体系中金属@载体界面位点与催化活性及稳定性之间的构效关系。
附:英文原文
Title: In Situ Exsolution of High-Density Ni Nanoparticles in LaAl0.3Mn0.2Ni0.5O3δ Cathode for the Electro-Thermocatalytic CO2-Intensified Dry Reforming of Methane
Author: Haolin Liu, Shuo Wang, Houfu Lv, Rongtan Li, Yuxiang Shen, Chaobin Zeng, Xiaomin Zhang, Yuefeng Song, Na Ta, Shaowei Zhang, Fang Lu, Guoxiong Wang, Xinhe Bao
Issue&Volume: December 11, 2025
Abstract: The tandem electro-thermocatalytic system, which integrates dry reforming of methane with reverse water–gas shift and H2O electrolysis reactions within a solid oxide electrolysis cell, offers an innovative path for the utilization of CO2-rich feedstocks. The identification of the correlation between the interface-dependent characteristics and both catalytic activity and stability remains a formidable challenge. Herein, we focus on the exsolution of high-density and well-dispersed nanoparticles semiembedded on the LaAl0.3Mn0.2Ni0.5O3δ cathode by modulating the Al and Mn co-doping strategy. The substantial and stable metal@perovskite interfacial sites exhibit high intrinsic activity for the tandem electro-thermocatalytic system, which provides high single-pass CO2 and CH4 conversion over 92%, syngas yield over 93%, apparent CH4 reducibility up to 3.91, and a CH4 turnover frequency of 73.77 molCH4 molNi–1 s–1 using various CO2-rich feedstocks (CO2/CH4 = 2–4) at 800 °C. In situ electrochemical diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy and density functional theory calculations demonstrate the crucial role of *OH electrolysis in the tandem catalysis process. This work elucidates the structure–activity relationship between the metal@support interfacial sites and catalytic activity and stability for the tandem electro-thermocatalytic system.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c09782
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c09782
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
