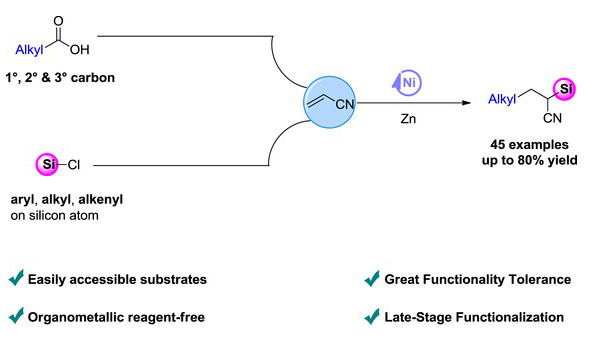
近日,大连理工大学张譞团队报道了镍催化丙烯腈与羧酸和氯硅烷还原烷基硅化反应制备烷基硅烷。2025年12月10日出版的《中国化学》杂志发表了这项成果。
过渡金属催化的烯烃与碳、硅亲电试剂的还原碳硅化反应,因其避免了传统方法中需要使用对空气和水分敏感的预制备有机金属试剂,近年来受到合成化学家的广泛关注。然而,当前可用的碳亲电试剂仅限于烷基或芳基溴化物。因此,开发通过选择更易获得的碳亲电试剂来实现的新合成策略仍具迫切需求。
研究组报道了一种镍催化方案,能够以氯硅烷和烷基羧酸通过N-羟基邻苯二甲酰亚胺(NHPI)酯的形式实现丙烯腈的烷基硅化,从而构建多种烷基硅烷。该方法采用储量丰富且易得的羧酸作为新型烷基亲电试剂来源,突破了现有局限。这代表了在烯烃还原硅化烷基化反应中首次使用羧酸作为烷基试剂,从而为合成多种结构多样的有机硅烷提供了对现有方法学的重要补充。
该策略还展现出广泛的底物适用范围(包括一级、二级和三级羧酸)、良好的官能团耐受性(可兼容卤素、杂环、Boc保护的胺基、酯基、酮基、末端及内烯烃和末端炔烃),并具备对复杂农用化学品和药物分子进行后续修饰的潜力。此外,克级规模反应进一步证明了所开发方法的实际应用潜力。总而言之,该方案不仅拓展了烯烃还原双官能化反应的边界,也丰富了烷基硅烷化合物制备的合成工具箱。
附:英文原文
Title: Access to Alkylsilanes via Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Alkylsilylation of Acrylonitrile with Carboxylic Acids and Chlorosilanes†
Author: Jinwei Sun, Ao Liu, Rui Gu, Xuan Zhang
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-10
Abstract: Transition-metal catalyzed reductive carbosilylation of alkenes with carbon and silyl electrophiles has gained considerable attention for synthetic chemists recently, because it avoids air- and moisture-sensitive pre-prepared organometallic reagents used. However, current carbon electrophiles are limited to alkyl or aryl bromides. Therefore, developing new synthetic approaches by choosing more easily available carbon electrophiles is still in high demand. Herein, we describe a nickel-catalyzed protocol that enables alkylsilylation of acrylonitrile with chlorosilanes and alkyl carboxylic acids via NHPI esters for the construction of various alkylsilanes, in which abundant and easy-accessible carboxylic acids were employed as the new alkyl electrophile sources, overcoming current limitations. This represents the first example of utilizing carboxylic acid as the alkyl reagent in reductive silylative alkylation of alkenes, thus providing a valuable complement to existing methodologies for the synthesis of a variety of organosilanes with diverse structures. Our approach also showcases broad substrate scope (including primary, secondary and tertiary carboxylic acids), good functional group compatibility (tolerating halides, heterocycles, Boc-protected amine, ester, ketone, terminal and internal alkenes, and terminal alkyne) and offers the capability for post-modification of complex agrochemical and pharmaceuticals. In addition, gram-scale reaction further demonstrates the applicable potential of the developed method. Overall, this protocol not only expands the boundaries of reductive difunctionalization reactions of alkenes but also enriches the synthetic toolbox for alkylsilane compounds preparation.
DOI: 10.1002/cjoc.70400
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cjoc.70400
Chinese Journal of Chemistry:《中国化学》,创刊于1983年。隶属于Wiley,最新IF:5.4
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/16147065
投稿链接:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/cjoc
