近日,中国科学院化学所韩布兴团队研究了高效氨基酸电合成中质子调节的C-N偶联。相关论文于2025年12月10日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
利用丰富氮源与α-酮酸电化学合成氨基酸是一条可持续路径。提高反应效率并探究其影响因素机制具有重要意义。
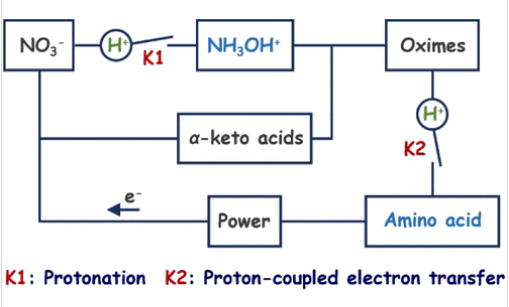
研究组分析了电解质中质子对氨基酸合成的影响——这一因素至今尚未被充分关注。以树枝状铋催化剂上草酸与硝酸盐共还原合成甘氨酸为模型体系,研究组发现优化的质子浓度能特异性增强四步反应中的两个关键步骤,从而调控甘氨酸选择性与产率。其一,质子直接参与硝酸盐还原关键中间体的配位过程,适宜的质子浓度促使NH2OH(代表吸附位点)以质子化形式NH3OH+从催化剂表面脱附,有效避免其进一步还原为NH3,从而保障甘氨酸合成所需的关键中间体。其二,合适的质子浓度有利于乙醛酸肼的质子耦合电子转移氢化反应生成甘氨酸,最终提升甘氨酸选择性与产率。
基于该机理认知的指导,研究组通过优化反应条件精确调控各关键步骤,实现了优异的甘氨酸电合成性能:法拉第效率达78.9%,分电流密度为108.2 mA cm-2。该方法的多功能性进一步通过高效合成丙氨酸、天冬氨酸及苯甘氨酸等多种氨基酸得到验证,均展现出极高的法拉第效率与产率。
附:英文原文
Title: Proton-Regulated C–N Coupling for Efficient Amino Acid Electrosynthesis
Author: Yong Wang, Xiang-Da Zhang, Pengsong Li, Congyang Wang, Yuqing Hou, Ran Duan, Jun Ma, Ganwen Zhang, Xihua Wang, Huizhen Liu, Yichao Zhang, Lihong Jing, Qingli Qian, Xiaofu Sun, Xinchen Kang, Qinggong Zhu, Buxing Han
Issue&Volume: December 10, 2025
Abstract: Electrosynthesis of amino acids from abundant nitrogen sources and α-keto acids represents a sustainable route. Enhancing the reaction efficiency and exploring the mechanisms influencing the reaction are of great significance. Herein, we studied the effect of protons in the electrolyte on amino acid synthesis, which has been overlooked to date. Using the coreduction of oxalic acid and nitrate (NO3–) to glycine (Gly) on dendritic Bi as a model system, we found that optimal proton concentrations specifically enhance two key steps of the four-step reactions, governing Gly selectivity and production rate. One is that protons directly coordinate with key intermediates in NO3– reduction. Suitable proton concentration induces the desorption of *NH2OH (where * denotes an adsorption site) as protonated NH3OH+ from the catalyst surface. This desorption effectively prevents *NH2OH from further reduction to NH3, securing the essential intermediate (NH3OH+) for Gly synthesis. The other is that suitable proton concentration favors the proton-coupled electron transfer hydrogenation of glyoxylic acid oxime to Gly, which finally enhances the Gly selectivity and production rate. Guided by this mechanistic insight, we optimized the reaction conditions to precisely control each critical step, achieving excellent Gly electrosynthesis performance with an FEGly of 78.9% and a partial current density of 108.2 mA cm–2. The versatility of this approach was further demonstrated through efficient synthesis of diverse amino acids, including alanine, aspartic acid, and phenylglycine, delivering very high FEs and yield rates.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c15446
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c15446
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
