近日,西南科技大学宋英泽团队揭示了废LiFePO4直接再生中的剩余电荷效应。相关论文发表在2025年12月9日出版的《德国应用化学》杂志上。
废旧锂离子电池安全破碎处理技术的出现,将使得未来回收产业中不完全放电磷酸铁锂(IDS-LFP)的比例显著增加。具有不同残余电荷的IDS-LFP与完全放电S-LFP(FDS-LFP)在微观结构和物理化学性质上存在差异。然而,现有直接再生研究主要集中于FDS-LFP,对IDS-LFP的再生机制及残余电荷与再生效果的关系关注不足。
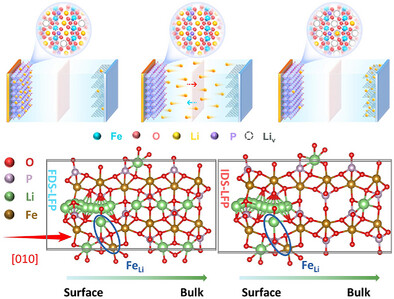
为此,研究组依据物理化学特性对FDS-LFP和IDS-LFP进行分类,并采用三种再生方法探究其修复过程的差异。与FDS-LFP相比,IDS-LFP因体相空位缺陷导致更高的锂嵌入能垒。此外,再生IDS-LFP(IDR-LFP)中FeLi反位缺陷比例(1.3%)高于再生FDS-LFP(FDR-LFP)(0.6%),证实IDS-LFP无法实现完全再生。因此,FDR-LFP在1C倍率下的放电比容量达137.1 mA h g−1,400次循环后容量保持率为81.5%;而IDR-LFP在相同条件下放电比容量仅为105.1 mA h g−1。该研究为处理不同残余电荷状态的S-LFP提供了基础性见解。
附:英文原文
Title: Unveiling Residual Charge Effects in the Direct Regeneration of Spent LiFePO4
Author: Changrui Lu, Yang Cao, Junfeng Li, Xiaofang Wang, Hechao Xu, Zhixin Wang, Qi Wan, Xijun Wei, Guangmin Zhou, Yingze Song
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-09
Abstract: The emergence of safe crushing technologies for spent lithium-ion batteries treatment will significantly increase the proportion of incompletely discharged spent LiFePO4 (IDS-LFP) in future recycling industry. The IDS-LFP and fully discharged S-LFP (FDS-LFP) with different residual charge show different microstructures and physicochemical properties. However, the current research in direct regeneration mainly focus on FDS-LFP, the regeneration of IDS-LFP and the relationship between residual charges and regeneration effect that has received less attention. Therefore, we classify the FDS-LFP and IDS-LFP based on their physicochemical properties and investigate the differences in their repair process using three kinds of regeneration methods. Compared to FDS-LFP, IDS-LFP exhibits a higher lithium intercalation energy barrier due to vacancies in the bulk. In addition, the proportion of FeLi anti-site defects in regenerated IDS-LFP (IDR-LFP) (1.3%) is higher than regenerated FDS-LFP (FDR-LFP) (0.6%), confirming that IDS-LFP cannot be completely regenerated. As a result, FDR-LFP delivers a specific discharge capacity of 137.1 mA h g1 at 1 C, retaining 81.5% capacity retention after 400 cycles. In sharp contrast, IDR-LFP only provides a specific discharge capacity of 105.1 mA h g1 at 1 C. This study provides foundational insights for handing S-LFP with varying residual charge.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202518557
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202518557
Angewandte Chemie:《德国应用化学》,创刊于1887年。隶属于德国化学会,最新IF:16.823
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213773
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/anie/default.aspx
