近日,北京大学窦锦虎团队实现了通过调节配体氧化态控制导电金属-有机框架中的包装顺序。相关论文于2025年12月8日发表在《德国应用化学》杂志上。
由金属节点和氧化还原活性配体组成的导电金属有机骨架(c-MOFs)由于其多孔性和电荷输运的共存而引起了学界越来越多的关注。值得注意的是,它们的电学性能与框架内的填料和配体氧化态密切相关,这一点很少被探索。典型的二价金属节点有利于与单一氧化态的配体形成饱和的层内方平面配位,从而预先确定了框架拓扑结构。
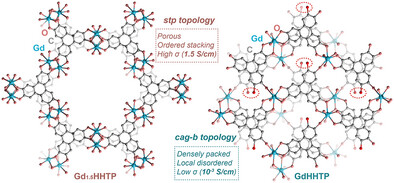
研究组报告了一种包装和拓扑控制策略,通过调整配体氧化态和基于镧系元素(如Gd)的通用配位化学来实现。Difftheme反射光谱和单晶输运测量表明,在低温下,Gd3+与2,3,6,7,10,11-六羟基三苯(HHTP)在较低的混合氧化态(4和5)得到更有序的多孔封装(Gd1.5HHTP),具有优越的电子传输性能。相反,在高温下,配体采用更高的氧化态(3),与Gd3+配位产生具有局部配位紊乱(GdHHTP)的致密排列结构,导致电导率显著降低。研究组表明,配体-氧化态调谐为精确控制c-MOFs的结构顺序和电荷输运提供了一种有效的策略,为合理设计具有可调谐电子性能的材料奠定了理论基础。
附:英文原文
Title: Packing Order Control in Conductive Metal–Organic Frameworks by Tuning Ligand Oxidation State
Author: Yunlong Fan, Bin Jiang, Zhenghan Zhang, Haoyang Zhang, Luming Yang, Tianyang Chen, Liu He, Yanjun Liu, Jinkun Guo, Tongyang Zhao, Ran Du, Cen Tang, Jian Li, Maojun Zheng, Jin-Hu Dou
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-08
Abstract: Conductive metal–organic frameworks (c-MOFs), composed of metal nodes and redox-active ligands, have attracted growing interest due to the coexistence of porosity and charge transport. Notably, their electrical performance is closely related to the packing and ligand oxidation state within the framework, which has rarely been explored. Typical divalent metal nodes favor saturated intralayer square-planar coordination to ligands in a single oxidation state, thereby predetermining the framework topology. Here, we report a packing and topology control strategy, achieved by tuning the ligand oxidation state and grounded in lanthanides (e.g., Gd) versatile coordination chemistry. Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy and single-crystal transport measurements reveal that, at low temperature, coordination of Gd3+ with 2,3,6,7,10,11-hexahydroxytriphenylene (HHTP) in a lower mixed oxidation state (4 and 5) yields a more ordered porous packing (Gd1.5HHTP) with superior electronic transport performance. In contrast, at elevated temperature, the ligand adopts a higher oxidation state (3), and coordination with Gd3+ yields a densely packed structure with local coordination disorder (GdHHTP), resulting in a markedly reduced electrical conductivity. This study demonstrates ligand-oxidation-state tuning provides an effective strategy for the precise control of structural order and charge transport in c-MOFs, laying a theoretical foundation for the rational design of materials with tunable electronic properties.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202522424
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202522424
Angewandte Chemie:《德国应用化学》,创刊于1887年。隶属于德国化学会,最新IF:16.823
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213773
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/anie/default.aspx
