斯坦福大学医学院Kari C. Nadeau小组的一项最新研究认为花生过敏口服免疫治疗驱动花生反应性T细胞单细胞多组学变化,与持续无反应性相关。2025年11月4日,国际知名学术期刊《自然—免疫学》发表了这一成果。
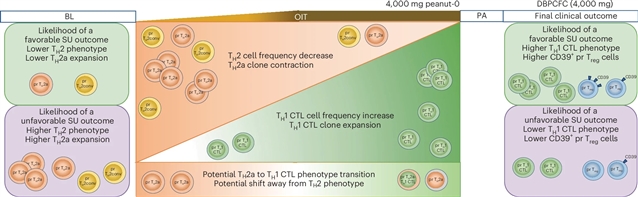
课题组研究人员分析了来自2期花生OIT试验队列的pr CD4+ T细胞的单细胞RNA和蛋白质免疫表型以及T细胞受体谱。该课题组研究人员发现在OIT期间细胞毒性相关表型和1型辅助细胞毒性T淋巴细胞样细胞克隆扩增增加,而2型辅助T (TH2)细胞相关表型和TH2样细胞克隆扩增减少。获得持续无反应性的OIT参与者的特点是,基线TH2相关表型较低,OIT后细胞毒性相关的pr效应T细胞基因特征升高,pr调节性T细胞中CD39表达较高。这些发现阐明了油脂诱导的CD4+ T细胞耐受机制,并可以指导有效的过敏原特异性油脂疗法。
据了解,口服免疫疗法(OIT)是美国食品和药物管理局批准的唯一治疗花生过敏的方法。花生反应性(pr) CD4+ T细胞在花生过敏发病机制和油脂诱导的脱敏中起关键作用。然而,导致OIT停药后持续无反应的潜在CD4+ T细胞免疫机制在很大程度上是未知的。
附:英文原文
Title: Peanut allergy oral immunotherapy drives single-cell multi-omic changes in peanut-reactive T cells associated with sustained unresponsiveness
Author: Han, Xiaorui, Skatova, Valeria, Mikelov, Artem, Ji, Xuhuai, Hoh, Ramona A., Lee, Ji-Yeun, Cao, Shu, Seastedt, Hana, Schuetz, Jackson, Fernandes, Andrea, Singhal, Arpita, Grubert, Fabian, DeKruyff, Rosemarie H., Maecker, Holden T., Galli, Stephen J., Manohar, Monali, Chinthrajah, R. Sharon, Kasowski, Maya M., Boyd, Scott D., Nadeau, Kari C.
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-04
Abstract: Oral immunotherapy (OIT) is the only U.S. Food and Drud Administration-approved treatment for peanut allergy. Peanut-reactive (pr) CD4+ T cells are pivotal in peanut allergy pathogenesis and OIT-induced desensitization. However, the underlying pr CD4+ T cell immune mechanisms leading to sustained unresponsiveness after OIT discontinuation are largely unknown. We analyzed single-cell RNA and protein immunophenotypes and T cell receptor repertoires of pr CD4+ T cells from a phase 2 peanut OIT trial cohort. We identified increased cytotoxicity-related phenotypes and type 1 helper cytotoxic T lymphocyte-like cell clonal expansion during OIT, while type 2 helper T (TH2) cell-related phenotypes and TH2-like cell clonal expansion decreased. OIT participants achieving sustained unresponsiveness were distinguished by lower baseline TH2-related phenotypes, elevated post-OIT cytotoxicity-related pr effector T cell gene signatures and higher CD39 expression in pr regulatory T cells. These findings clarify OIT-induced CD4+ T cell tolerance mechanisms and can guide effective allergen-specific OIT strategies.
DOI: 10.1038/s41590-025-02323-3
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41590-025-02323-3
Nature Immunology:《自然—免疫学》,创刊于2000年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:31.25
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/ni/
投稿链接:https://mts-ni.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
