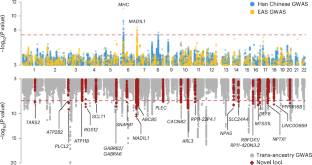
中国科学院昆明动物研究所李明研究组在研究中取得进展。他们报道了东亚和欧洲人群双相情感障碍的跨祖先全基因组分析改进了遗传发现。相关论文发表在2025年11月25日出版的《自然—神经科学》杂志上。
在这里,该研究团队对汉族个体(5164例和13460例对照)进行了BD的GWAS,并与来自PGC4 GWAS的独立东亚(EAS, 4479例和75725例对照)和欧洲(59287例和781022例对照)队列进行了比较和综合分析。他们在EAS祖先中的GWAS鉴定出两个全基因组显著风险位点,包括主要组织相容性复合体(MHC) II类区域的变异。将EAS数据整合到跨祖先GWAS中,发现了93个显著位点(23个新位点)。遗传力富集分析涉及多种神经元细胞类型。多维GWAS后优先级确定了39个高可信度风险基因,其中15个在BD患者的大脑中差异表达,12个在小鼠中调节BD相关行为,18个在药理学上是可处理的。这项工作促进了对双相障碍生物学基础的理解,并为未来在代表性不足的人群中的研究提供了方向。作者进行了一项汉族双相情感障碍(BD)全基因组关联研究,并整合了东亚和欧洲的PGC4数据集,发现了23个新的基因座,优先考虑了39个可信的风险基因,并提示了与BD相关的细胞类型和药物靶点。
研究人员表示,双相情感障碍(BD)的全基因组关联研究(GWASs)主要包括欧洲(EUR)血统的个体,未充分代表非EUR人群,并且限制了对疾病机制的了解。
附:英文原文
Title: Trans-ancestry genome-wide analyses of bipolar disorder in East Asian and European populations improve genetic discovery
Author: Zhang, Chu-Yi, Li, Miao, Sun, Ping, Hui, Li, Gao, Yuan, Yang, Jian-Zhong, Zhang, Nan, Feng, Xiaoyang, Wu, Yong, Guo, Lei, Yuan, Jing, Jiang, Hong-Yan, Cheng, Yu-Qi, Ma, Simeng, Gong, Qian, Sun, Yaoyao, Li, Yi, Qu, Na, Yin, Xu-Yuan, Wang, Lu, Yang, Yongfeng, Wang, Chuansheng, Lv, Luxian, Zhou, Dongsheng, Li, Xingxing, Chen, Xiaogang, Zhang, Chen, Chen, Jun, Song, Xueqin, Tang, Jinsong, Cai, Jun, Fan, Weixing, Tang, Wei, Tang, Wenxin, Li, Wenqiang, Tang, Xia, Zhang, Xiaoxi, Lu, Yan, Yao, Yong-Gang, Wang, Chuang, So, Hon-Cheong, Iwata, Nakao, Ikeda, Masashi, Saito, Takeo, Liu, Zhongchun, Xu, Shuahua, Yue, Weihua, Fang, Yiru, Zhu, Feng, Xiao, Xiao, Li, Ming
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-25
Abstract: Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) of bipolar disorder (BD) have predominantly included individuals of European (EUR) ancestry, underrepresenting non-EUR populations and limiting insight into disease mechanisms. Here we performed a GWAS of BD in Han Chinese individuals (5,164 cases and 13,460 controls) and conducted comparative and integrative analyses with independent East Asian (EAS, 4,479 cases and 75,725 controls) and EUR (59,287 cases and 781,022 controls) cohorts from the PGC4 GWAS. Our GWAS in EAS ancestry identified two genome-wide significant risk loci, including variants at the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II region. Incorporating EAS data into trans-ancestry GWAS revealed 93 significant loci (23 novel). Heritability enrichment analyses implicated a variety of neuronal cell types. Multidimensional post-GWAS prioritization identified 39 high-confidence risk genes, of which 15 were differentially expressed in the brains of patients with BD, 12 modulated BD-relevant behaviors in mice and 18 are pharmacologically tractable. This work advances understanding of the biological underpinnings of BD and provides direction for future research in underrepresented populations. The authors conducted a genome-wide association study of bipolar disorder (BD) in Han Chinese and integrated PGC4 East Asian and European datasets, discovering 23 novel loci, prioritizing 39 credible risk genes and implicating BD-related cell types and druggable targets.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-025-02147-2
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-025-02147-2
Nature Neuroscience:《自然—神经科学》,创刊于1998年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:28.771
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/neuro/
投稿链接:https://mts-nn.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
