近日,澳大利亚墨尔本大学教授Bradley J. Turner及其课题组报道了在散发性ALS患者的iPSC衍生运动神经元中进行大规模药物筛选,确定了一种潜在的组合疗法。该项研究成果发表在2025年11月24日出版的《自然—神经科学》上。
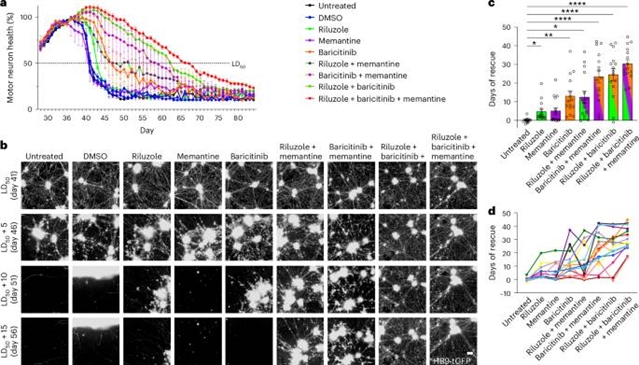
在这里,该团队从100例散发性ALS (SALS)患者中建立了iPSC文库,并进行了全人群表型筛选。来自SALS患者的运动神经元再现了该疾病的关键方面,包括生存期缩短、与供体生存相关的神经突退化加速、转录失调和利鲁唑的药理拯救。先前在ALS临床试验中测试的药物筛选显示,97%的药物未能减轻神经退行性变,反映了试验结果并验证了SALS模型。有效药物的组合试验确定巴西替尼、美金刚和利鲁唑是一种有前途的治疗SALS的药物组合。这些发现表明,患者来源的iPSC模型可以概括散发性疾病的特征,为ALS的新一代疾病建模和治疗发现铺平了道路。在这项研究中,作者从100多例散发性ALS病例中生成了iPSC系,再现了关键的疾病表型,并进行了大规模的药物筛选,确定了巴西替尼、美金刚和利鲁唑的联合治疗。
据介绍,异质性和主要散发的神经退行性疾病,如肌萎缩性侧索硬化症(ALS),仍然具有很高的挑战性。患者源性诱导多能干细胞(iPSC)技术为这些疾病提供了巨大的希望;然而,证明散发性疾病患者神经退化加速的大规模研究是有限的。
附:英文原文
Title: Large-scale drug screening in iPSC-derived motor neurons from sporadic ALS patients identifies a potential combinatorial therapy
Author: Bye, Christopher R., Qian, Elizabeth, Lim, Katherine, Daniszewski, Maciej, Garton, Fleur C., Trn-L, Bo C., Liang, Helena H., Lin, Tian, Lock, John G., Crombie, Duncan E., Morgan, Steven, Hu, Yi, Barton, Samantha K., Palmer, Lucy M., Djouma, Elvan, Kodikara, Saritha, L Cao, Kim-Anh, Dharmadasa, Thanuja, Henders, Anjali K., Ziser, Laura A., Kiernan, Matthew C., Talbot, Kevin, Needham, Merrilee, Fletcher, Susan, Talman, Paul, Mathers, Susan, Wray, Naomi R., Hewitt, Alex W., Pebay, Alice, Turner, Bradley J.
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-24
Abstract: Heterogeneous and predominantly sporadic neurodegenerative diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), remain highly challenging to model. Patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technologies offer great promise for these diseases; however, large-scale studies demonstrating accelerated neurodegeneration in patients with sporadic disease are limited. Here we generated an iPSC library from 100 patients with sporadic ALS (SALS) and conducted population-wide phenotypic screening. Motor neurons derived from patients with SALS recapitulated key aspects of the disease, including reduced survival, accelerated neurite degeneration correlating with donor survival, transcriptional dysregulation and pharmacological rescue by riluzole. Screening of drugs previously tested in ALS clinical trials revealed that 97% failed to mitigate neurodegeneration, reflecting trial outcomes and validating the SALS model. Combinatorial testing of effective drugs identified baricitinib, memantine and riluzole as a promising therapeutic combination for SALS. These findings demonstrate that patient-derived iPSC models can recapitulate sporadic disease features, paving the way for a new generation of disease modeling and therapeutic discovery in ALS. In this study, the authors generated iPSC lines from more than 100 sporadic ALS cases, which recapitulated key disease phenotypes and enabled large-scale drug screening, identifying a promising combination therapy of baricitinib, memantine and riluzole.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-025-02118-7
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-025-02118-7
Nature Neuroscience:《自然—神经科学》,创刊于1998年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:28.771
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/neuro/
投稿链接:https://mts-nn.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
