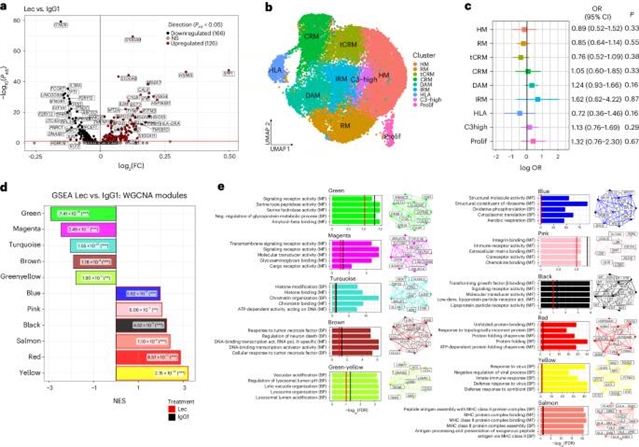
法兰德斯生物技术研究所Bart De Strooper课题组在研究中取得进展。他们揭示了阿尔茨海默氏症治疗药物Lecanemab通过诱导小胶质细胞中的淀粉样蛋白清除程序来减轻Aβ病理。该研究于2025年11月24日发表于国际一流学术期刊《自然—神经科学》杂志上。
在这里,该研究团队证明Lecanemab,一种领先的抗β-淀粉样蛋白(a β)抗体,通过激活小胶质效应功能介导淀粉样蛋白清除。使用人类小胶质细胞异种移植同种主题模型,小组发现Lecanemab显著降低了a β病理和相关的神经损伤,而片段结晶(Fc)沉默的Lecanemab和小胶质细胞缺乏都不能引起这种作用,尽管斑块结合完整。单细胞RNA测序和空间转录组学分析显示,Lecanemab诱导了一个聚焦的转录程序,增强了吞噬作用、溶酶体降解、代谢重编程、干扰素γ基因和抗原呈递。最后,该课题组确定了SPP1/骨桥蛋白是由Lecanemab治疗诱导的一个主要因子,并证明了其在促进a β清除中的作用。这些发现强调,有效的淀粉样蛋白去除依赖于小胶质细胞通过Fc片段的参与,为优化阿尔茨海默病的抗淀粉样蛋白疗法提供了重要的见解。
据悉,关于抗淀粉样蛋白免疫疗法的争议强调了阐明其作用机制的必要性。
附:英文原文
Title: The Alzheimer’s therapeutic Lecanemab attenuates Aβ pathology by inducing an amyloid-clearing program in microglia
Author: Albertini, Giulia, Zielonka, Magdalena, Cuypers, Marie-Lynn, Snellinx, An, Xu, Ciana, Poovathingal, Suresh, Wojno, Marta, Davie, Kristofer, van Lieshout, Veerle, Craessaerts, Katleen, Wolfs, Leen, Pasciuto, Emanuela, Jaspers, Tom, Horr, Katrien, Serneels, Lurgarde, Fiers, Mark, Dewilde, Maarten, De Strooper, Bart
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-24
Abstract: Controversies over anti-amyloid immunotherapies underscore the need to elucidate their mechanisms of action. Here we demonstrate that Lecanemab, a leading anti-β-amyloid (Aβ) antibody, mediates amyloid clearance by activating microglial effector functions. Using a human microglia xenograft mouse model, we show that Lecanemab significantly reduces Aβ pathology and associated neuritic damage, while neither fragment crystallizable (Fc)-silenced Lecanemab nor microglia deficiency elicits this effect despite intact plaque binding. Single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomic analyses reveal that Lecanemab induces a focused transcriptional program that enhances phagocytosis, lysosomal degradation, metabolic reprogramming, interferon γ genes and antigen presentation. Finally, we identify SPP1/osteopontin as a major factor induced by Lecanemab treatment and demonstrate its role in promoting Aβ clearance. These findings highlight that effective amyloid removal depends on the engagement of microglia through the Fc fragment, providing critical insights for optimizing anti-amyloid therapies in Alzheimer’s disease.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-025-02125-8
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-025-02125-8
Nature Neuroscience:《自然—神经科学》,创刊于1998年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:28.771
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/neuro/
投稿链接:https://mts-nn.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
