近日,南京大学郑鹏团队报道了通过最大化氢键的超稳定蛋白质的计算设计。相关论文发表在2025年11月18日出版的《自然-化学》杂志上。
氢键作为稳定蛋白质结构的基础化学相互作用,尤其在β折叠片中能赋予蛋白质抵抗机械应力与极端环境的能力。
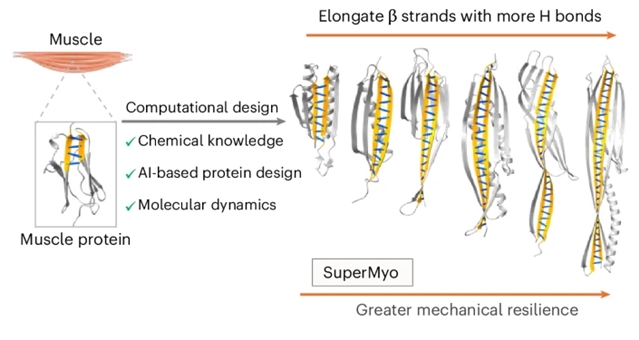
受天然具有剪切氢键的机械稳定性蛋白质(如肌联蛋白和丝素蛋白)的启发,研究组通过最大化受力β链内的氢键网络,从头设计了超稳定蛋白质。利用结合人工智能引导结构与序列设计的计算框架,以及全原子分子动力学模拟,研究组系统性地拓展了蛋白质架构,将主链氢键数量从4个增加至33个。
所得蛋白质的解折叠力超过1000皮牛,比天然肌联蛋白免疫球蛋白结构域强约400%,并在150°C高温暴露后仍能保持结构完整性。这种分子层面的稳定性直接转化为宏观性能,表现为可形成热稳定水凝胶。该研究提出了一种可扩展的高效计算策略,用于设计强韧蛋白质,为极端环境下的韧性蛋白质系统理性设计提供了普适性方法。
附:英文原文
Title: Computational design of superstable proteins through maximized hydrogen bonding
Author: Zheng, Bin, Lu, Zhuojian, Wang, Shangchen, Liu, Lichao, Ao, Mingjun, Zhou, Yurui, Tang, Guojing, Wang, Ruishi, Liu, Yuanhao, Zhang, Hantian, Meng, Yinying, Qiu, Jun, Feng, Tianfu, Wang, Ziyi, Liu, Renming, Xiao, Yuelong, Liu, Yutong, Wang, Ziling, Huang, Yifen, Jiang, Yajun, Zheng, Peng
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-18
Abstract: Hydrogen bonds are fundamental chemical interactions that stabilize protein structures, particularly in β sheets, enabling resistance to mechanical stress and environmental extremes. Here, inspired by natural mechanostable proteins with shearing hydrogen bonds, such as titin and silk fibroin, we de novo designed superstable proteins by maximizing hydrogen-bond networks within force-bearing β strands. Using a computational framework combining artificial intelligence-guided structure and sequence design with all-atom molecular dynamics MD simulations, we systematically expanded protein architecture, increasing the number of backbone hydrogen bonds from 4 to 33. The resulting proteins exhibited unfolding forces exceeding 1,000pN, about 400% stronger than the natural titin immunoglobulin domain, and retained structural integrity after exposure to 150°C. This molecular-level stability translated directly to macroscopic properties, as demonstrated by the formation of thermally stable hydrogels. Our work introduces a scalable and efficient computational strategy for engineering robust proteins, offering a generalizable approach for the rational design of resilient protein systems for extreme environments.
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01998-3
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-01998-3
Nature Chemistry:《自然—化学》,创刊于2009年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:24.274
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nchem/
投稿链接:https://mts-nchem.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
