近日,美国加州大学戴维斯分校Joshua Hihath团队制定了控制DNA电荷传输的设计指南。该项研究成果发表在2025年11月18日出版的《自然-化学》杂志上。
描述分子电子结构的概念框架是理解化学结构、反应机理及设计有机化合物不可或缺的理论工具。
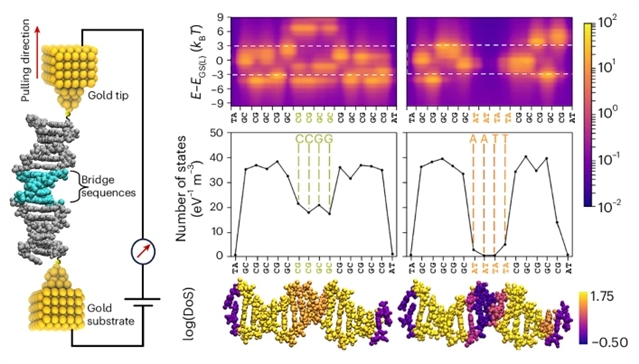
研究组针对DNA分子电子结构的调控,初步建立了一套设计原则。近期研究表明,电荷离域可跨越数个碱基发生,导致相干长度超越单个碱基对的范围。为探究碱基间相互作用及其对电荷离域的影响,研究组重点考察在以鸟嘌呤-胞嘧啶碱基对为主的DNA双链中,相邻碱基对相互作用对电荷传输特性的影响。
研究结果表明,通过精确调控序列排列,可在不改变分子组成的前提下显著改变导电性能。进而通过分析电子态密度,推导出一套旨在维持长链DNA双螺旋高电导值的设计准则。基于这些规则,研究组成功展示了20碱基对DNA序列可实现超过1×10-3 G0的电导值。
附:英文原文
Title: Developing design guidelines for controlling charge transport in DNA
Author: Aminiranjbar, Zahra, Akin Gultakti, Caglanaz, Zhang, Amy, Oren, Ersin Emre, Hihath, Joshua
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-18
Abstract: Conceptual frameworks that describe the electronic structure of molecules are an integral part of understanding chemical structures and reaction mechanisms and designing organic compounds. Here we develop a preliminary set of design guidelines for controlling the electronic structure of DNA. Recent work indicates that charge delocalization occurs over several bases and results in coherence lengths greater than a single base pair. To examine the interactions between bases and their effects on delocalization, this study investigates the influence of nearest-neighbour base pair interactions on the charge transport properties of DNA duplexes that are predominantly composed of guanine–cytosine base pairs. Results show that, by manipulating the sequence, the conductance can be substantially modified without altering the molecular composition. The electronic density of states are then analysed to deduce a set of design guidelines aimed at maintaining high conductance values in long duplexes. Utilizing these rules, we demonstrate that 20-base-pair DNA sequences can exhibit conductance values surpassing 1×103G0.
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01999-2
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-01999-2
Nature Chemistry:《自然—化学》,创刊于2009年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:24.274
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nchem/
投稿链接:https://mts-nchem.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
