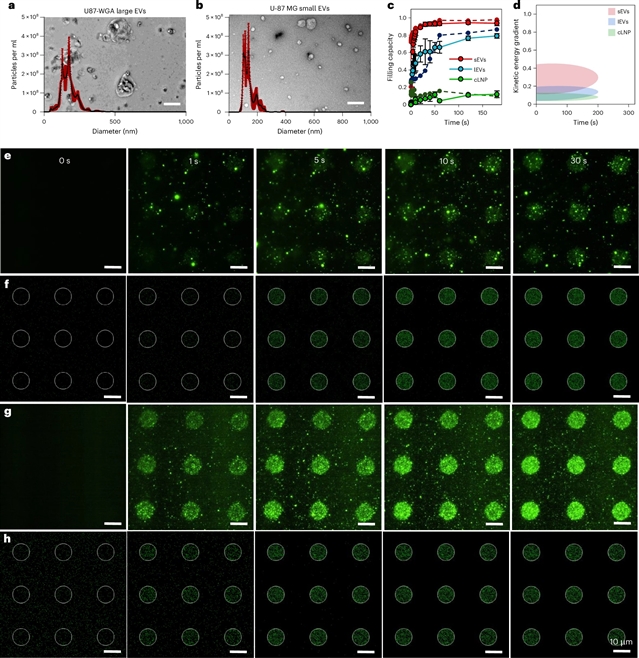
俄亥俄州立大学Eduardo Reátegui小组宣布他们研制了光诱导的细胞外囊泡和颗粒吸附。这一研究成果发表在2025年11月18日出版的国际学术期刊《自然—方法学》上。
课题组引入了光诱导细胞外囊泡和颗粒吸附(LEVA)作为研究表面结合EVPs的有力解决方案。LEVA的多功能性在GFP-EV标准、传统和生物反应器培养的EVs、DiFi外显子和埃希氏菌大肠杆菌,其结果模式主题为单EV荧光成像,细胞迁移在迁移小体模拟路径和细菌EV介导的中性粒细胞聚集。LEVA将迅速推进他们对细胞外基质蛋白和表面结合EVPs的理解,并将鼓励来自许多学科的研究人员创造新的仿生、免疫工程和其他检测方法。
研究人员表示,在过去的二十年中,细胞外囊泡(EVs)和细胞外颗粒(EPs/EVPs)在人类健康和疾病中的作用引起了相当大的关注。然而,虽然已知几种类型的EVP与细胞外基质动态相互作用,并且在产生高保真EVP微模式方面具有巨大的潜在价值,但目前还没有具有这种能力的无标签、可扩展和可调的平台技术。
附:英文原文
Title: Light-induced extracellular vesicle and particle adsorption
Author: Hisey, Colin L., Rima, Xilal Y., Doon-Ralls, Jacob, Nagaraj, Chiranth K., Mayone, Sophia, Nguyen, Kim Truc, Wiggins, Sydney, Dorayappan, Kalpana Deepa Priya, Huang, Xin, Hade, Mangesh D., Selvendiran, Karuppaiyah, Higginbotham, James N., Tutanov, Oleg, Franklin, Jeffrey L., Coffey, Robert J., Wood, David, Hu, Chunyu, Patel, Divya S., Magaa, Setty M., Palmer, Andre F., Hansford, Derek, Retegui, Eduardo
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-18
Abstract: The role of extracellular vesicles (EVs) and particles (EPs/EVPs) in human health and disease has garnered considerable attention over the past two decades. However, while several types of EVPs are known to interact dynamically with the extracellular matrix and there is great potential value in producing high-fidelity EVP micropatterns, there are currently no label-free, scalable and tunable platform technologies with this capability. We introduce light-induced extracellular vesicle and particle adsorption (LEVA) as a powerful solution to study surface-bound EVPs. The versatility of LEVA is demonstrated using GFP–EV standards, EVs from conventional and bioreactor cultures, DiFi exomeres and Escherichiacoli EVs, with the resulting patterns used for single-EV fluorescence imaging, cell migration on migrasome-mimetic trails and bacterial EV-mediated neutrophil swarming. LEVA will rapidly advance our understanding of extracellular matrix protein- and surface-bound EVPs and should encourage researchers from many disciplines to create new biomimetic, immunoengineering and other assays.
DOI: 10.1038/s41592-025-02914-w
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-025-02914-w
Nature Methods:《自然—方法学》,创刊于2004年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:47.99
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nmeth/
投稿链接:https://mts-nmeth.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
