近日,中国科学院国家纳米科学中心王浩团队研究了用于肿瘤特异性铁死亡的六聚体连接体双作用纳米PROTAC的全新设计。2025年11月13日出版的《德国应用化学》杂志发表了这项成果。
蛋白降解靶向嵌合体(PROTAC)技术作为药物研发领域的突破性策略,通过利用泛素-蛋白酶体系统实现疾病相关蛋白的定向降解。其效能主要取决于连接链的设计——这一关键结构显著影响三元复合物(靶蛋白-PROTAC-E3连接酶)的稳定性与药代动力学特性。然而,由于复杂的构效关系与繁琐的合成过程,针对不同靶点的连接链优化仍面临挑战。
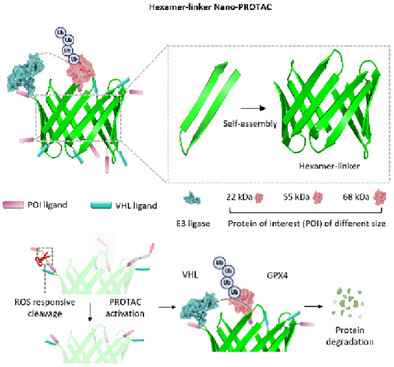
研究组开发了一种自组装六聚体连接链纳米PROTAC,其能自主调控空间距离,从而实现对不同尺寸蛋白的高效降解。这种桶状六聚体连接链具有极广的普适性,可降解多种尺寸蛋白(如22、55及68 kDa),降解效率高达99%。更重要的是,相较于线性连接链,该自组装六聚体连接链的血浆稳定性提升了48倍。
通过构建兼具表皮生长因子受体靶向与活性氧响应性的"双门控"系统纳米PROTAC,在小鼠模型中成功实现了难降解蛋白谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4的清除,诱导肿瘤特异性铁死亡并降低脱靶毒性。这种具有空间自适应能力的六聚体连接链纳米PROTAC体系为简化PROTAC开发提供了普适性策略,彰显了其在靶向蛋白降解治疗领域的变革性潜力。
附:英文原文
Title: De Novo Design of Hexamer-Linker Dual-Action Nano-PROTAC for Tumor-Specific Ferroptosis
Author: Ni-Yuan Zhang, Zhuan Wen, Ming-Ze Cai, Ke-Ting Zhou, Hao-Ze Li, Yi-xuan Liu, Shang Wu, Yu Xia, Hong-Wei An, Hao Wang
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-13
Abstract: Proteolysis-Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) technology, a groundbreaking approach in drug discovery, leverages the ubiquitin-proteasome system to degrade disease-related proteins. Its efficacy mainly hinges on the linker design, which critically influences ternary complex (target protein-PROTAC-E3 ligase) stability and pharmacokinetics. However, optimizing linkers for diverse targets remains challenging due to complex structure-activity relationships and laborious synthesis processes. Herein, we developed a self-assembled hexamer-linker Nano-PROTACs, which was capable of self-regulating spatial distances, enabling efficient degradation of proteins with different sizes. This barrel-like hexamer-linker has a very wide range of universality, enabling the degradation of multiple size proteins (e.g., 22, 55 and 68 kDa), with a degradation efficiency of up to 99%. More importantly, compared to a linear linker, the plasma stability of this self-assembled hexamer-linker increased by 48 times. Using Nano-PROTAC with “double-gated” system combining epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) targeting and ROS-responsiveness, degradation of the challenging protein glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) was achieved on mouse models, inducing tumor-specific ferroptosis with reduced off-target toxicity. This spatially adaptable hexamer-linker Nano-PROTAC system offers a universal strategy to streamline PROTAC development, highlighting its transformative potential for targeted protein degradation therapeutics.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202509924
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202509924
Angewandte Chemie:《德国应用化学》,创刊于1887年。隶属于德国化学会,最新IF:16.823
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213773
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/anie/default.aspx
