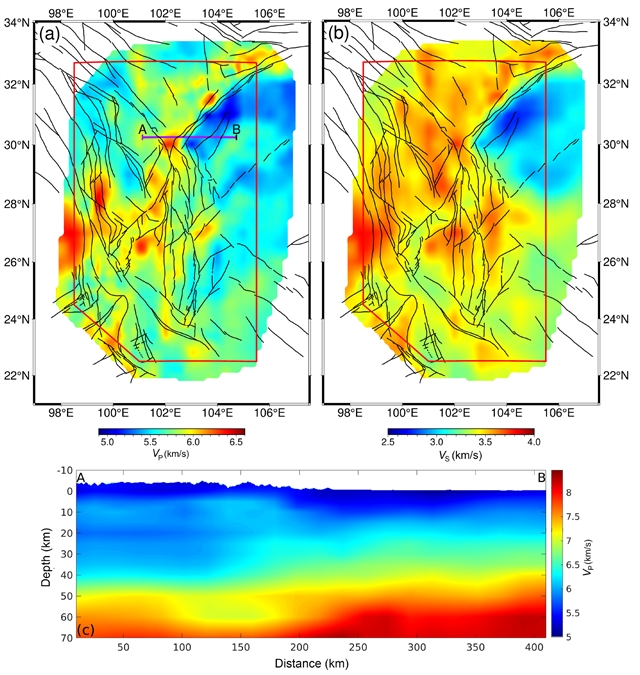
近日,中国科学技术大学李俊伦团队报道了基于地形高分辨率三维速度模型和地震波形匹配约束的川滇地区历史中强地震新一代震源机制目录。该项研究成果发表在2025年11月11日出版的《中国科学:地球科学》杂志上。
川滇地区发育有众多空间分布复杂、交汇关系错综复杂的大型活动断层,中强地震频发。获取这些地震的震源机制解,不仅对于分析区域地壳应力场、断层几何形态、活动习性和地震潜势至关重要,也对评估地震灾害具有关键意义。以往研究基于一维地壳速度模型获得了区域历史中强地震的震源机制目录,或基于考虑横向变化的三维速度模型反演了少数代表性事件的震源机制。然而,对于川滇地区,一个融合了区域高分辨率三维速度模型与显著地形起伏的系统性震源机制反演框架仍然缺失。
研究组利用包含区域地形起伏的高分辨率三维速度模型SWChinaCVM-2.0,首先为遍布川滇地区的181个永久宽频带地震台站构建了一个全面的应变格林张量库。具体而言,正演模拟采用了震源-接收点互易性理论和谱元法,并对计算得到的库进行了高效压缩。随后,利用全波形匹配方法,对2009-2021年间该区域内发生的563次ML≥4级地震进行了系统性的震源机制反演。通过得到的断层平面解、全矩张量和矩震级,研究组获得了一个新一代的、精确的川滇地区中强地震震源机制目录。该目录可为未来川滇地区的地球科学研究提供基础性数据,也是一项由新技术和新方法驱动的基础性地球物理工作。未来,该反演框架也可应用于华北、新疆等地震高风险区,为震源参数的快速精确测定和地震灾害评估提供重要支撑。
附:英文原文
Title: A new-generation source mechanism catalogue for historical moderate-to-strong earthquakes in the Sichuan-Yunnan region constrained by a topographic high-resolution 3D velocity model and seismic waveform matching
Author: Chang GUO, Junlun LI, Weiwei WU, Huajian Yao
Issue&Volume: 2025/11/11
Abstract: The Sichuan-Yunnan region hosts numerous large active faults with complex spatial distributions and intricate intersections, where moderate-to-strong earthquakes occur frequently. Obtaining source mechanism solutions for these earthquakes is not only essential for analyzing the regional crustal stress regime, fault geometries, activity behaviors and seismic potentials, but also is critical for assessing seismic hazards. Previous studies have obtained source mechanism catalogs of regional historical moderate-to-strong earthquakes based on 1D crustal velocity models, or inverted source mechanisms for few representative events based on 3D velocity models incorporating lateral variations. However, a systematic source mechanism inversion framework, which integrates regional high-resolution 3D velocity models with significant topographic relief, still remains absent for the Sichuan-Yunnan region. Using the high-resolution 3D velocity model SWChinaCVM-2.0 with regional topographic relief, we first construct a comprehensive strain Green’s tensor library for the 181 permanent broadband seismic stations across the Sichuan-Yunnan region. In particular, the forward modeling employs the spectral element method (SEM) with source-receiver reciprocity, followed by highly efficient compression of the computed library. Subsequently, a systematic source mechanism inversion is conducted for the 563 ML≥4 earthquakes occurring in the region during 20092021 using full waveform matching. With the derived solutions of fault planes, full moment tensors and moment magnitudes, a new-generation, accurate source mechanism catalog for moderate-to-strong earthquakes in the Sichuan-Yunnan region is obtained. This catalog can provide essential data for future geoscience studies in the Sichuan-Yunnan region, and is a foundational geophysical work driven by new techniques and methods. In the future, the inversion framework can also be applied to areas with high seismic risks such as North China and Xinjiang, providing essential supports for rapid and accurate determination of source parameters and assessment of seismic hazards.
DOI: 10.1007/s11430-024-1688-3
Source: https://www.sciengine.com/SCES/doi/10.1007/s11430-024-1688-3
Science China Earth Sciences:《中国科学:地球科学》,创刊于1952年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:5.7
官方网址:https://www.sciengine.com/SCES/home
投稿链接:https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/sces
