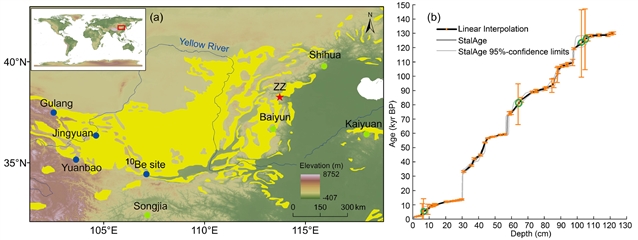
近日,湖南师范大学饶志国团队研究了过去13万年来华北珍珠洞石笋微量元素/钙记录揭示的东亚夏季风降水量演化。2025年11月13日出版的《中国科学:地球科学》杂志发表了这项成果。
在轨道时间尺度上,有观点认为,华中地区石笋的稳定氧同位素(δ18O)记录与华北黄土-古土壤序列重建的东亚夏季风(EASM)强度/降水量记录呈现出不同的变化模式。
研究组重建了华北珍珠洞石笋PS1在过去13万年以来高分辨率的微量元素/钙比值(Mg/Ca, Sr/Ca, Ba/Ca, Al/Ca, P/Ca)。基于珍珠洞两年的监测结果以及各微量元素/钙比值之间的相互关系,研究组证实PS1的Mg/Ca比值可以作为当地有效降水的一个稳健指标。
石笋PS1的Mg/Ca与δ13C记录在千年至轨道时间尺度上表现出高度的同位相协同变化,并在过去13万年间展现出一致的长期趋势,这一现象也得到了中国黄土高原西部基于黄土的EASM降水量记录的支持。这些相似性表明,珍珠洞地区的有效降水主要受控于华北地区的EASM降水量,同时也支持了EASM降水量的长期变化趋势,即从海洋同位素阶段(MIS)5e、5c、5a到MIS3时期递减,随后在MIS1时期(全新世)回升。过去13万年间华北EASM降水量的这一长期变化趋势,主要受太阳辐射和全球冰量的驱动。这些结果证实,在同一区域(如华北)内,来自石笋和黄土-古土壤剖面的、具有相同指示意义的代用指标可以相互印证。
附:英文原文
Title: Evolution of East Asian summer monsoon precipitation amount over the past 130 kyr recorded by stalagmite trace element/Ca records from Zhenzhu Cave, North China
Author: Yiping TIAN, Yunxia LI, Zhiguo RAO, Hai CHENG
Issue&Volume: 2025/11/13
Abstract: On orbital timescales, stable oxygen isotope (δ18O) records from stalagmites in Central China and East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) intensity/precipitation amount records reconstructed from loess-paleosol sequences in North China, have been suggested to show different change patterns. Here, high-resolution trace element/Ca ratios (Mg/Ca, Sr/Ca, Ba/Ca, Al/Ca, P/Ca) of stalagmite PS1 from Zhenzhu (ZZ) cave in North China over the past 130kyr have been reconstructed. Based on two years of monitoring results from ZZ cave and the relationships among trace element/Ca ratios, it is demonstrated that the PS1 Mg/Ca could be a robust indicator of local effective precipitation. The Mg/Ca and δ13C records of stalagmite PS1 exhibit highly in-phase co-variations on multi-millennial to orbital timescales and consistent long-term trends over the past 130kyr, which is supported by the loess-based EASM precipitation amount records from the western Chinese Loess Plateau. These similarities indicate that effective precipitation of the ZZ cave area is mainly controlled by EASM precipitation amount in North China, and also support the long-term variation trend of the EASM precipitation amount, that is, decreasing from marine isotope stage (MIS) 5e–MIS5c–MIS5a–MIS3, followed by an increase to MIS1. This long-term variation trend of EASM precipitation amount in North China over the past 130kyr is primarily driven by solar insolation and global ice volume. These results confirm that proxies with the same indicative significance from both stalagmites and loess-paleosol profiles within the same region (such as North China) can corroborate each other.
DOI: 10.1007/s11430-025-1716-9
Source: https://www.sciengine.com/SCES/doi/10.1007/s11430-025-1716-9
Science China Earth Sciences:《中国科学:地球科学》,创刊于1952年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:5.7
官方网址:https://www.sciengine.com/SCES/home
投稿链接:https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/sces
