美国犹他大学医学院Scott A. Summers团队宣布他们的论文发现了神经酰胺脊骨的治疗性重塑可预防肾损伤。相关论文于2025年11月12日发表于国际顶尖学术期刊《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
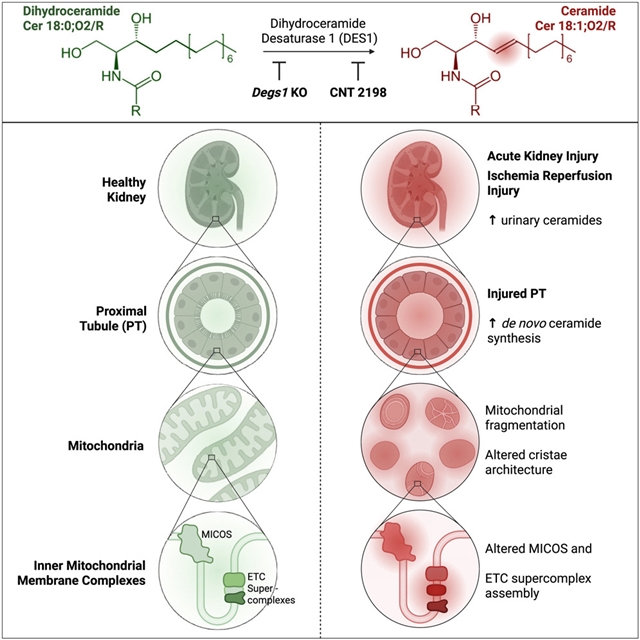
研究人员发现AKI诱导人类和小鼠PTs内脂毒性神经酰胺的生物合成,并且尿神经酰胺预测儿童和成人疾病的严重程度。对原发性PTs的机制研究,包括神经酰胺效应物的热蛋白质组学分析,揭示了神经酰胺改变线粒体接触部位、嵴组织系统(MICOS)和呼吸超复合体的组装,导致嵴结构、线粒体形态和呼吸的急性破坏。这些神经酰胺的作用依赖于由二氢神经酰胺去饱和酶1(DES1)插入的4,5-反式双键的存在。基因消融DES1可保护小鼠双侧缺血再灌注后的线粒体完整性并防止肾损伤。
此外,作为有吸引力的临床候选药物的新型DES1抑制剂也出现了DES1基因敲除现象。这些研究描述了AKI中PT线粒体损伤的一种新的、治疗上可处理的机制。
研究人员表示,近端小管(PT)脂质代谢的扰动促进了急性肾损伤(AKI)的病理特征。
附:英文原文
Title: Therapeutic remodeling of the ceramide backbone prevents kidney injury
Author: Rebekah J. Nicholson, Luis Cedeo-Rosario, J. Alan Maschek, Trevor Lonergan, Jonathan G. Van Vranken, Angela R.S. Kruse, Chris J. Stubben, Liping Wang, Deborah Stuart, Queren A. Alcantara, Monica P. Revelo, Kate Rutter, Mayette Pahulu, Jacob Taloa, Xuanchen Wu, Juwan Kim, Juna Kim, Isaac Hall, Amanda J. Clark, Samir Parikh, Jeffrey Spraggins, Donna Romero, Jeremy T. Blitzer, Steven P. Gygi, Jared Rutter, William L. Holland, Nirupama Ramkumar, Scott A. Summers
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-12
Abstract: Perturbation of proximal tubule (PT) lipid metabolism fuels the pathological features of acute kidney injury (AKI). We found that AKI induced biosynthesis of lipotoxic ceramides within PTs in humans and mice and that urine ceramides predicted disease severity in children and adults. Mechanistic studies in primary PTs, which included a thermal proteomic profiling screen for ceramide effectors, revealed that ceramides altered assembly of the mitochondrial contact site and cristae-organizing system (MICOS) and respiratory supercomplexes, leading to acute disruption of cristae architecture, mitochondrial morphology, and respiration. These ceramide actions were dependent on the presence of the 4,5-trans double bond inserted by dihydroceramide desaturase 1 (DES1). Genetically ablating DES1 preserved mitochondrial integrity and prevented kidney injury in mice following bilateral ischemia reperfusion. Moreover, novel DES1 inhibitors that are attractive clinical drug candidates phenocopied the DES1 knockouts. These studies describe a new, therapeutically tractable mechanism underlying PT mitochondrial damage in AKI.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.10.006
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00440-1
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
