美国肯塔基大学Lance A. Johnson团队的最新研究提出了小鼠APOE4到APOE2等位基因转换改善阿尔茨海默病相关代谢特征、神经病理学和认知。这一研究成果发表在2025年11月11日出版的国际学术期刊《自然—神经科学》上。
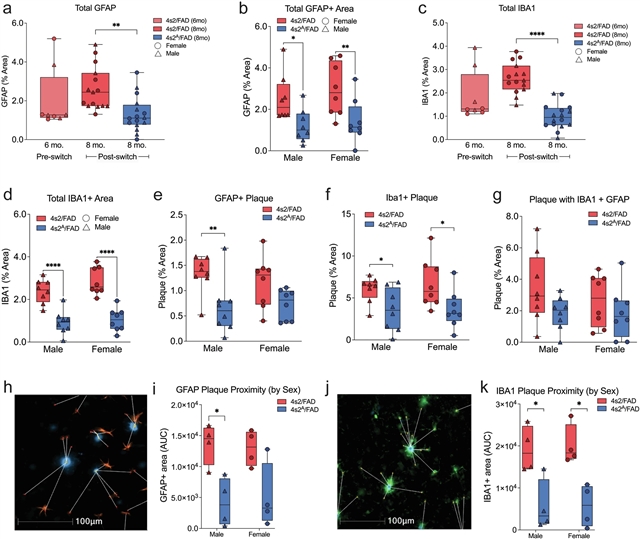
在这里,该课题组研究人员开发了一种敲入模型,允许在风险等位基因和保护等位基因(APOE4s2)之间进行可诱导的“切换”。基因表达和蛋白质组学分析证实,APOE4s2小鼠在基线时合成E4,给药后合成E2。全身等位基因开关导致类似于E2/E2人类的代谢谱,并驱动脂质组和单细胞转录组中AD相关的改变,特别是在星形胶质细胞中。最后,当交叉到5xFAD背景时,星形胶质细胞特异性E4到E2转换改善认知,减少淀粉样蛋白病理,降低胶质细胞增生,减少斑块相关载脂蛋白E。这些数据表明,从APOE4到APOE2的短期过渡可以广泛影响大脑转录组和脂质组,星形胶质细胞特异性APOE替代可能是未来基因编辑方法的可行策略,可以同时减少多种AD相关病理。
据了解,与携带两个载脂蛋白E (APOE)等位基因ε4拷贝的个体相比,ε2纯合子的晚发型阿尔茨海默病(AD)风险降低了约99%。
附:英文原文
Title: APOE4 to APOE2 allelic switching in mice improves Alzheimer’s disease-related metabolic signatures, neuropathology and cognition
Author: Golden, Lesley R., Siano, Dahlia S., Stephens, Isaiah O., MacLean, Steven M., Saito, Kai, Nolt, Georgia L., Funnell, Jessica L., Pallerla, Akhil V., Lee, Sangderk, Smith, Cathryn, Chen, Jing, Zhu, Haining, Voy, Clairity, Whitus, Callie M., Hernandez, Gabriela, Farmer, Brandon C., Pandya, Kumar, Cowley, Dale O., Macauley, Shannon L., Gordon, Scott M., Morganti, Josh M., Johnson, Lance A.
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-11
Abstract: Compared to individuals carrying two copies of the ε4 allele of apolipoprotein E (APOE), ε2 homozygotes have an approximate 99% reduction in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD) risk. Here we develop a knock-in model that allows for an inducible ‘switch’ between risk and protective alleles (APOE4s2). Gene expression and proteomic analyses confirm that APOE4s2 mice synthesize E4 at baseline and E2 after tamoxifen administration. A whole-body allelic switch results in a metabolic profile resembling E2/E2 humans and drives AD-relevant alterations in the lipidome and single-cell transcriptome, particularly in astrocytes. Finally, when crossed to the 5xFAD background, astrocyte-specific E4 to E2 switching improves cognition, decreases amyloid pathology, lowers gliosis and reduces plaque-associated apolipoprotein E. Together, these data show that a short-term transition from APOE4 to APOE2 can broadly affect the cerebral transcriptome and lipidome, and that astrocyte-specific APOE replacement may be a viable strategy for future gene editing approaches to simultaneously reduce multiple AD-associated pathologies.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-025-02094-y
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-025-02094-y
Nature Neuroscience:《自然—神经科学》,创刊于1998年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:28.771
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/neuro/
投稿链接:https://mts-nn.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
