英国剑桥大学Jason S. Carroll研究组提出了转录因子转换驱动亚型特异性胰腺癌。这一研究成果于2025年10月30日发表在国际顶尖学术期刊《自然—遗传学》上。
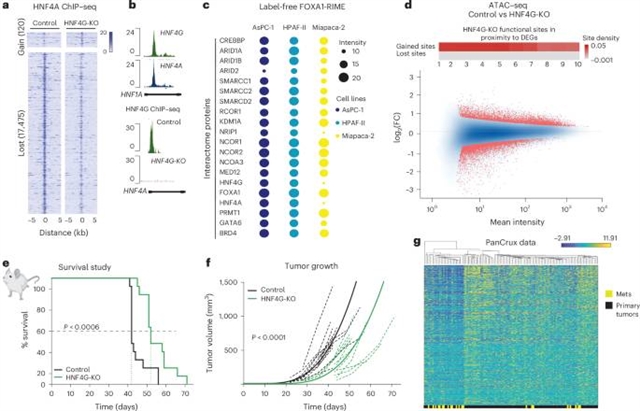
该团队发现了一种转录因子开关机制,涉及特征不明确的孤儿核受体HNF4G和假定的先驱因子FOXA1,它们驱动PDAC的进展。利用他们的无偏蛋白相互作用组发现方法,研究组在临床前模型和惠普尔手术样本中发现了HNF4A和HNF4G是可重复的FOXA1相关蛋白。在原发性肿瘤背景下,课题组研究人员一致发现主要的转录因子是HNF4G,它在其中起驱动作用。一种分子开关发生在疾病晚期,HNF4G的表达或活性降低,揭示了FOXA1的转录潜力。低表达的FOXA1通过协调转移特异性增强子-启动子环来调节转移基因的表达,从而驱动晚期疾病。HNF4G和FOXA1活性分别在原发肿瘤生长和转移中影响总生存。研究组认为,由分子区隔化引发的阶段依赖性转录因子活性的存在介导了PDAC的进展。
据介绍,新出现的证据表明,谱系特异性转录因子控制胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)的进展。
附:英文原文
Title: Transcription factor switching drives subtype-specific pancreatic cancer
Author: Rao, Shalini V., Young, Lisa, Cheeseman, Danya, Flynn, Sean, Krebs, Niklas, Couturier, Dominique-Laurent, Mack, Stephanie, Brais, Rebecca, Temple, Jill, Smith, Amy, Papachristou, Evangelia, Pelicano, Catarina, Chilamakuri, Chandra Sekhar Reddy, Herka, Krzysztof, Baba, Hideo, Farah, Luay, Cheung, Phyllis F., Siveke, Jens, Guerrier, Stphane, Insolia, Luca, Gill, Michael, Archer Goode, Emily, Kupczak, Steven, Cheng, Yi, Borsari, Giacomo, Jodrell, Duncan, DSantos, Clive, Russell, Alasdair, Grnwald, Barbara T., Serrao, Eva, Chernukhin, Igor, Carroll, Jason S.
Issue&Volume: 2025-10-30
Abstract: Emerging evidence suggests that lineage-specifying transcription factors control the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). We have discovered a transcription factor switching mechanism involving the poorly characterized orphan nuclear receptor HNF4G and the putative pioneer factor FOXA1, which drives PDAC progression. Using our unbiased protein interactome discovery approach, we identified HNF4A and HNF4G as reproducible, FOXA1-associated proteins, in both preclinical models and Whipple surgical samples. In the primary tumor context, we consistently find that the dominant transcription factor is HNF4G, where it functions as the driver. A molecular switch occurs in advanced disease, whereby HNF4G expression or activity decreases, unmasking FOXA1’s transcriptional potential. Derepressed FOXA1 drives late-stage disease by orchestrating metastasis-specific enhancer–promoter loops to regulate the expression of metastatic genes. Overall survival is influenced by HNF4G and FOXA1 activity in primary tumor growth and in metastasis, respectively. We suggest that the existence of stage-dependent transcription factor activity, triggered by molecular compartmentalization, mediates the progression of PDAC.
DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02389-7
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-025-02389-7
Nature Genetics:《自然—遗传学》,创刊于1992年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:41.307
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/ng/
投稿链接:https://mts-ng.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
