生物质原料用于制造高性能聚合物可以帮助扩大其应用范围,减少对有限化石资源的依赖。然而,提高生物基聚酯的耐热性和亲水性仍然是一个重大的挑战。
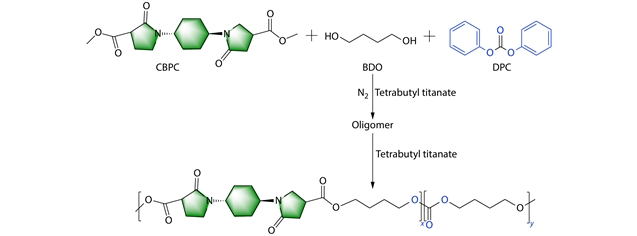
研究组制备了一种新型生物基三环二酸酯N,N';-反式-1,4-环己烷-双(吡咯烷酮-4-甲基羧酸酯)(CBPC),它是由可再生衣康酸二甲基和反式-1,4-环己烷二胺通过aza-Michael加成反应合成的。作为一种独特的共聚单体,CBPC具有刚性的三环主链,显著提高了链的填充性和热稳定性,而其吡咯烷酮侧基具有可调的极性和改善的亲水性。以CBPC、碳酸二苯酯和1,4-丁二醇为原料,通过酯交换和熔融缩聚法制备了CBPC含量为10 mol% ~ 30 mol%的PBCC共聚物。
CBPC的加入将熔融温度(Tm)从56.8°C提高到225.8°C,将初始分解温度(Td5%)从258.0°C提高到306.7°C,使PBCC成为目前报道的最耐热的生物基聚酯之一。此外,吡咯烷酮单元实现了从疏水到亲水的转化。该研究表明,CBPC是设计具有增强热学和表面性能的生物基聚合物的有效和创新的构建块,为开发高性能可持续材料提供了有前景的策略。
附:英文原文
Title: An Excellent Biobased Copolymerization Monomer Module: Synthesis of Biobased Copolymers with Excellent Heat Resistance and Hydrophilic Properties
Author: Xiao-Jun Ma, Xiao-Qing Hao, Hong-Ji Wang, Han-Yu Yao, Zi-Qing Wang, Yin Lv
Issue&Volume: 2025-10-23
Abstract: The use of biomass feedstocks for the manufacture of high-performance polymers can help expand their range of applications and reduce their dependence on finite fossil resources. However, improving the heat resistance and hydrophilicity of bio-based polyesters remains a significant challenge. Herein, we introduce N,N'-trans-1,4-cyclohexane-bis(pyrrolidone-4-methylcarboxylate) (CBPC), a novel bio-based tricyclic dibasic ester synthesized from renewable dimethyl itaconic acid and trans-1,4-cyclohexane diamine via an aza-Michael addition reaction. As a unique comonomer, CBPC features a rigid tricyclic backbone that significantly enhances chain packing and thermal stability, whereas its pyrrolidone side groups impart tunable polarity and improved hydrophilicity. Using CBPC, diphenyl carbonate, and 1,4-butylene glycol, a series of PBCC copolymers with 10 mol%–30 mol% CBPC was synthesized via ester-exchange and melt polycondensation methods. Incorporation of CBPC raised the melting temperature (Tm) from 56.8 °C to 225.8 °C and the initial decomposition temperature (Td5%) from 258.0 °C to 306.7 °C, positioning PBCC among the most heat-resistant bio-based polyesters reported. Additionally, the pyrrolidone units enabled transformation from hydrophobic to hydrophilic. This study demonstrates that CBPC is an effective and innovative building block for the design of bio-based polymers with enhanced thermal and surface properties, offering a promising strategy for the development of high-performance sustainable materials.
DOI: 10.1007/s10118-025-3433-4
Source: https://www.cjps.org/en/article/doi/10.1007/s10118-025-3433-4/
Chinese Journal of Polymer Science:《中国高分子科学杂志》,创刊于1983年。隶属于中国化学会,最新IF:4.3
官方网址:https://www.cjps.org/
投稿链接:https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/cjps
