近日,清华大学李景虹团队研究了基于多重保证催化DNA计算电路的可编程癌症亚型评估器。2025年10月22日出版的《美国化学会志》发表了这项成果。
异质性乳腺癌的分子亚型分类对于个性化治疗至关重要,但传统的单靶点诊断系统的低特异性限制了这一点。
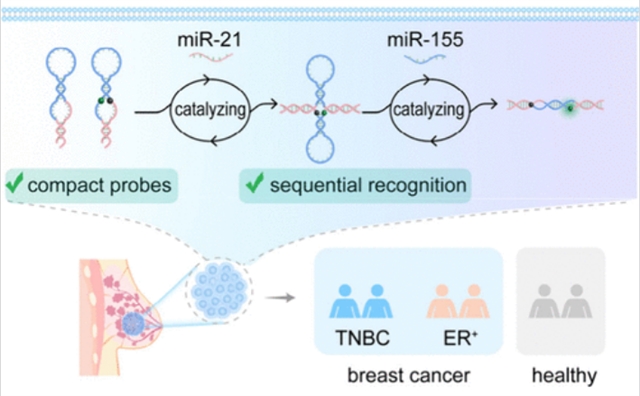
研究组开发了一种紧凑和通用的催化DNA计算(CDC)电路,作为一种可编程的癌症评估器,用于高效的双微小RNA (miRNA)检测,通过顺序扩增的多路分子成像技术,可以在临床样品中精确识别乳腺癌亚型。采用创新和精致的探针连接和接枝策略,紧凑的CDC系统以最小的链复杂性设计,仅包含两个串联笼状探针,形成两个不同的催化发夹组装(CHA)电路模块:CDC前和CDC后模块。这些基于CHA的模块被多个miRNA依次激活,从而实现局部级联信号放大,用于癌症亚型评估。
通过系统的实验验证和互补的理论模拟,研究组阐明了顺序反应机理,并发现上游前CDC模块对下游后CDC模块激活的反应动力学约束。这些发现为分子反应过程提供了有价值的见解,并为设计高效的CDC探针提供了重要指导。凭借其全面的多分析物识别和协同级联扩增能力,紧凑的CDC电路能够放大检测癌细胞内的多种miRNA。CDC平台在识别临床癌症组织方面表现出卓越的特异性,使其成为乳腺癌的最佳癌细胞亚型评估器。该分子评估仪具有较高的准确性和可靠性,在临床诊断和疾病相关分子机制研究中具有潜在的应用前景。
附:英文原文
Title: Programmable Cancer Subtype Evaluator via Multiply-Guaranteed Catalytic DNA Computing Circuit
Author: Ruomeng Li, Xue Gong, Jinhua Shang, Yuqian Jiang, Weizhen Chen, Gaosong Wu, Xiaoqing Liu, Fuan Wang, Jinghong Li
Issue&Volume: October 22, 2025
Abstract: Molecular subtype classification of heterogeneous breast cancer is crucial for personalized therapies yet is limited by the low specificity of conventional single-target diagnosis systems. Herein, we developed a compact and versatile catalytic DNA computing (CDC) circuit as a programmable cancer evaluator for efficient dual-microRNA (miRNA) detection, enabling precise breast cancer subtype identification in clinical samples through a sequentially amplified multiplexed molecular imaging technique. Using an innovative and exquisite probe-concatenating and grafting strategy, the compact CDC system was engineered with minimal strand complexity, incorporating only two tandem-caged probes to form two distinct catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) circuitry modules: pre-CDC and post-CDC modules. These CHA-based modules were sequentially activated by multiple miRNAs, enabling localized cascade signal amplification for the cancer subtype evaluation. Through systematic experimental validation and complementary theoretical simulations, we elucidated the sequential reaction mechanism and discovered the reaction kinetic confinement of the upstream pre-CDC module on the downstream post-CDC module activation. These findings provided valuable insights into the molecular reaction processes and offered critical guidance for designing efficient CDC probes. With its comprehensive multianalyte recognition and synergistic cascade amplification capabilities, the compact CDC circuit enabled the magnified detection of multiple miRNAs within cancer cells. The CDC platform demonstrated exceptional specificity in identifying clinical cancer tissues, making it a robust cancer cell subtype evaluator for breast cancer. Due to its high accuracy and reliability, this molecular evaluator serves as a promising diagnostic tool with potential applications in clinical diagnosis and disease-related molecular mechanism studies.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c13399
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c13399
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
