路德维希癌症研究所Joshua D. Rabinowitz研究团队取得一项新突破。他们提出了老年小鼠表现出广泛的代谢变化,但保留了主要的通量。该研究于2025年10月16日发表于国际一流学术期刊《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
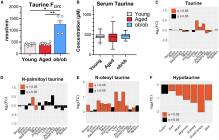
课题组通过代谢组学和稳定同位素示踪研究了小鼠年龄诱导的代谢改变。测量了年轻和年老(20-30个月)C57BL/6J小鼠的循环代谢物通量、血清和组织浓度,并以年轻肥胖(ob/ob)小鼠为对照。对于主要循环代谢物,浓度随年龄的变化大于通量的变化,通量随肥胖的变化大于随衰老的变化。具体来说,葡萄糖、乳酸、3-羟基丁酸和许多氨基酸(但不包括牛磺酸)的浓度随着年龄的增长而显著变化。只有谷氨酰胺循环通量这样做。尽管潜在的代谢变化,主要循环代谢物的通量保持稳定。例如,赖氨酸的分解代谢从糖精途径转向细果酸途径,而细果酸的浓度和通量都随着年龄的增长而增加。其他较少的代谢物也表现出一致的、年龄引起的浓度和通量变化。虽然衰老导致了广泛的代谢变化,但主要的代谢通量在很大程度上保留了下来。
研究人员表示,代谢失调是衰老的标志。
附:英文原文
Title: Aged mice exhibit widespread metabolic changes but preserved major fluxes
Author: Connor S.R. Jankowski, Laith Z. Samarah, Michael R. MacArthur, Sarah J. Mitchell, Daniel R. Weilandt, Craig J. Hunter, Xianfeng Zeng, Melanie R. McReynolds, Joshua D. Rabinowitz
Issue&Volume: 2025-10-16
Abstract: Metabolic dysregulation is a hallmark of aging. Here, we investigate in mice age-induced metabolic alterations using metabolomics and stable isotope tracing. Circulating metabolite fluxes and serum and tissue concentrations were measured in young and old (20–30 months) C57BL/6J mice, with young obese (ob/ob) mice as a comparator. For major circulating metabolites, concentrations changed more with age than fluxes, and fluxes changed more with obesity than with aging. Specifically, glucose, lactate, 3-hydroxybutryate, and many amino acids (but notably not taurine) change significantly in concentration with age. Only glutamine circulatory flux does so. The fluxes of major circulating metabolites remain stable despite underlying metabolic changes. For example, lysine catabolism shifts from the saccharopine toward the pipecolic acid pathway, and both pipecolic acid concentration and flux increase with aging. Other less-abundant metabolites also show coherent, age-induced concentration and flux changes. Thus, while aging leads to widespread metabolic changes, major metabolic fluxes are largely preserved.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.09.009
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00394-8
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
