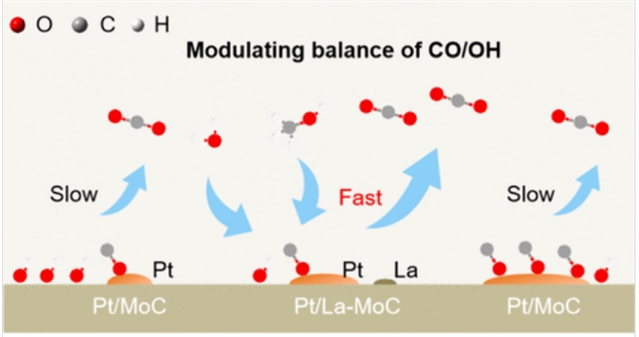
铂基催化剂上的电催化甲醇氧化反应(MOR)对可再生能源应用至关重要。然而,其性能常受限于CO中毒和活性位点利用率不足的问题。通过微环境调控来实现CO与OH中间体的动力学平衡,已成为解决上述局限的有效策略。
研究组开发了一种负载于镧掺杂碳化钼(La-MoC)载体上的铂催化剂,该体系利用α-MoC卓越的水解离能力持续提供丰富OH物种,同时通过La掺杂和Pt负载量精准调控表面覆盖度。这种双重微环境调控机制在Pt位点的CO与MoC位点的OH之间建立了最佳比例,从而加速CO氧化并最大化反应动力学。
所制备的Pt/La-MoC催化剂展现出8.58 A mgPt–1的卓越质量活性(达到商业Pt/C的3.6倍)、优异的稳定性(在0.1 M KOH中运行120小时后保持92%活性,在1 M KOH中运行30小时后保持80%活性)以及较低的CO氧化起始电位(~0.2 V vs RHE)。原位光谱与电化学研究证实,CO与OH中间体的协同循环促进了CO的快速去除与活性位点的再生。该工作提出了以中间体平衡为核心的理性设计理念,为理解电催化表面反应动力学提供了新视角。
附:英文原文
Title: Balanced CO/OH Intermediates for Efficient and CO-Resilient Electrocatalytic Methanol Oxidation via Pt Supported on La-Doped α-MoC
Author: Weiqin Wei, Xingjie Peng, Qingqing Zhou, Maolin Wang, Haoyi Tang, Junzhong Xie, Shuheng Tian, Wu Zhou, Xiao Ren, Ding Ma
Issue&Volume: October 14, 2025
Abstract: The electrocatalytic methanol oxidation reaction (MOR) over Pt-based catalysts is critical for renewable energy applications. However, its performance is often hampered by CO poisoning and the inefficient utilization of active sites. Regulating the kinetic balance of the CO and OH intermediates through microenvironmental control has emerged as an effective strategy to mitigate these limitations. Here, we present a Pt catalyst supported on lanthanum-doped molybdenum carbide (La-MoC), which leverages the exceptional water-dissociation capability of α-MoC to supply abundant OH species, while precisely controlling the surface coverage through La doping and Pt loading. This dual microenvironmental modulation establishes an optimal ratio between CO on Pt and OH on MoC, thereby accelerating CO oxidation and maximizing reaction kinetics. The resulting Pt/La-MoC catalyst exhibits a remarkable mass activity of 8.58 A mgPt–1 (3.6× higher than commercial Pt/C), excellent stability (92% activity retention after 120 h in 0.1 M KOH and 80% activity retention after 30 h in 1 M KOH), and a low CO oxidation onset potential (~0.2 V vs RHE). In situ spectroscopic and electrochemical studies confirm that the synchronized cycling of CO and OH intermediates promotes rapid CO removal and active-site regeneration. This work provides a rational design concept centered on intermediate balance, offering new insights into the dynamics of surface reactions in electrocatalysis.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c11866
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c11866
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
