近日,韩国成均馆大学Kim, Inki团队报道了基于多焦超透镜的图像扫描显微镜在脑类器官亚衍射限制成像中的应用。相关论文发表在2025年10月13日出版的《光:科学与应用》杂志上。
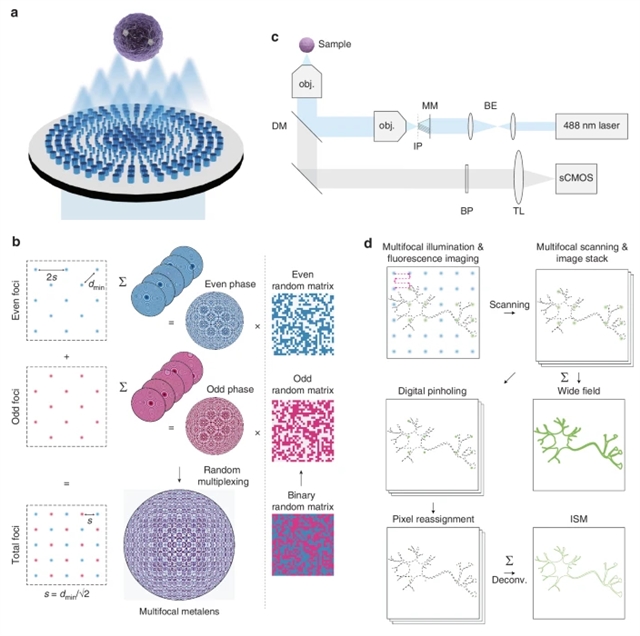
图像扫描显微镜(ISM)是一种很有前景的成像技术,提供亚衍射极限分辨率和光学切片。理论上,ISM可以通过像素重分配和反卷积将光学分辨率提高两倍。多焦阵列照明和扫描因其简单而被广泛用于实现ISM。传统上,数字微镜器件(DMDs)和微透镜阵列(MLAs)的应用为ISM生成密集均匀的多焦阵列,这是实现快速成像和高质量重建ISM的关键。然而,这些方法在成本、数值孔径(NA)、间距和均匀性方面存在局限性,使得在高NA下创建密集和高质量的多焦点阵列具有挑战性。
为了克服这些限制,研究组提出了一种新的多焦点超透镜设计策略,称为混合多路复用方法,它结合了两种传统的多路复用方法:相位加和随机多路复用。通过数值模拟,研究组证明即使在小间距条件下,所提出的方法也能比传统技术产生更均匀、更密集的多焦点阵列。作为概念验证,他们制备出一种多焦点超透镜,可在488纳米工作波长下生成40×40焦点阵列,其间距为3微米,数值孔径达0.7,并据此构建了多焦点超透镜集成扫描显微镜(MMISM)。
实验表明,该MMISM系统在微球样本和前脑类器官切片成像中成功分辨出亚衍射极限的细微结构。结果显示,与宽场成像相比,MMISM成像实现了两倍于衍射极限的分辨率,并呈现出更清晰的神经元结构特征。研究组预期这种新颖的设计策略可广泛应用于多功能光学元件的制备,并在特定应用中替代传统光学元件。
附:英文原文
Title: Image scanning microscopy based on multifocal metalens for sub-diffraction-limited imaging of brain organoids
Author: Jo, Yongjae, Park, Hyemi, Lee, Seho, Yoon, Hyeyoung, Lee, Taehoon, Bak, Gyusoo, Cho, Hanjun, Park, Jong-Chan, Kim, Inki
Issue&Volume: 2025-10-13
Abstract: Image scanning microscopy (ISM) is a promising imaging technique that offers sub-diffraction-limited resolution and optical sectioning. Theoretically, ISM can improve the optical resolution by a factor of two through pixel reassignment and deconvolution. Multifocal array illumination and scanning have been widely adopted to implement ISM because of their simplicity. Conventionally, digital micromirror devices (DMDs)1 and microlens arrays (MLAs)2,3 have been used to generate dense and uniform multifocal arrays for ISM, which are critical for achieving fast imaging and high-quality ISM reconstruction. However, these approaches have limitations in terms of cost, numerical aperture (NA), pitch, and uniformity, making it challenging to create dense and high-quality multifocal arrays at high NA. To overcome these limitations, we introduced a novel multifocal metalens design strategy called the hybrid multiplexing method, which combines two conventional multiplexing approaches: phase addition and random multiplexing. Through numerical simulations, we demonstrate that the proposed method generates more uniform and denser multifocal arrays than conventional methods, even at small pitches. As a proof of concept, we fabricated a multifocal metalens generating 40×40 array of foci with a 3μm pitch and NA of 0.7 operating at a wavelength of 488nm and then constructed the multifocal metalens-based ISM (MMISM). We demonstrated that MMISM successfully resolved sub-diffraction-limited features in imaging of microbead samples and forebrain organoid sections. The results showed that MMISM imaging achieved twice the diffraction-limited resolution and revealed clearer structural features of neurons compared to wide-field images. We anticipate that our novel design strategy can be widely applied to produce multifunctional optical elements and replace conventional optical elements in specialized applications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01900-3
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01900-3
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
