近日,中国科学院上海药物研究所柳红团队实现了预靶向线粒体输送有机砷用于癌症免疫治疗。这一研究成果发表在2025年10月13日出版的《美国化学会志》上。
线粒体靶向有机砷化合物显示出癌症治疗的潜力,但目前的给药方法面临着重大挑战,如肿瘤选择性差和全身毒性,导致剂量限制的副作用和治疗效果降低。
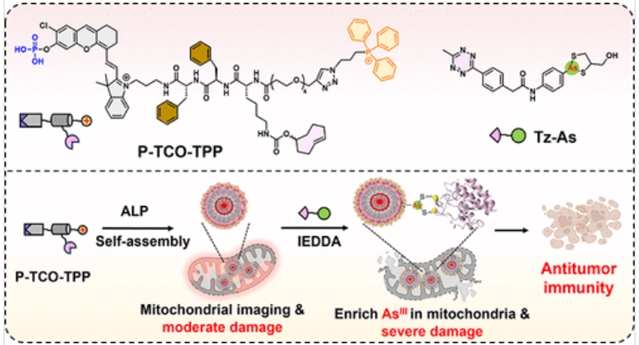
研究组提出了一种亚细胞预靶向递送策略,旨在选择性和有效地在肿瘤细胞线粒体内积累有机砷治疗药物。该方法利用P-TCO-TPP,一种碱性磷酸酶(ALP)响应小分子探针,含有磷酸盐笼型近红外merocyanine荧光团、反式环烯(TCO)和三苯基磷酸(TPP)基团。这使得线粒体靶向纳米颗粒在ALP介导的去磷酸化上的原位自组装成为可能。这些线粒体定位的纳米颗粒然后通过生物正交反电子需求Diels-Alder (IEDDA)反应快速捕获四氮-砷偶联物(Tz-As),导致线粒体砷积累增加5倍。这反过来又导致线粒体蛋白标记、硫氧还蛋白还原酶抑制、严重的线粒体功能障碍和肿瘤细胞的免疫原性细胞死亡。
值得注意的是,该策略在皮下宫颈癌HeLa和原位乳房4T1肿瘤模型中均具有较强的抗肿瘤功效,且毒性最小。此外,将该策略与抗PD-L1免疫治疗相结合,可在40%的小鼠中诱导4T1肿瘤完全消退,延长生存期,并几乎阻止肺转移。这种亚细胞预靶向策略为精确的线粒体药物递送提供了一个机器人平台,增强了各种细胞毒性药物在癌症免疫治疗中的治疗潜力。
附:英文原文
Title: Pretargeted Mitochondrial Delivery of Organoarsenicals for Cancer Immunotherapy
Author: Run Wang, Yuyang Tian, Xuliang Lu, Leyi Fang, Yinxing Miao, Daqing Fang, Yingxia Li, Hong Liu, Deju Ye
Issue&Volume: October 13, 2025
Abstract: Mitochondrial targeting of organoarsenic compounds shows potential for cancer therapy, but current delivery approaches face significant challenges such as poor tumor selectivity and systemic toxicity, leading to dose-limiting side effects and reduced therapeutic efficacy. In this study, we present a subcellular pretargeted delivery strategy designed to selectively and efficiently accumulate organoarsenic therapeutics within tumor cell mitochondria. This approach leverages P-TCO-TPP, an alkaline phosphatase (ALP)-responsive small-molecule probe containing a phosphate-caged near-infrared merocyanine fluorophore, trans-cyclooctene (TCO), and triphenylphosphonium (TPP) groups. This enables the in situ self-assembly of mitochondria-targeting nanoparticles upon ALP-mediated dephosphorylation. These mitochondria-localized nanoparticles then rapidly capture tetrazine-arsenic conjugates (Tz-As) via bioorthogonal inverse electron demand Diels–Alder (IEDDA) reaction, resulting in a >5-fold increase in mitochondrial arsenic accumulation. This, in turn, leads to mitochondrial proteins labeling, thioredoxin reductase inhibition, severe mitochondrial dysfunction, and immunogenic cell death in tumor cells. Notably, this strategy achieves strong antitumor efficacy with minimal toxicity in both subcutaneous cervical HeLa and orthotopic breast 4T1 tumor models. Furthermore, combining this strategy with anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy induces complete 4T1 tumor regression in 40% of mice, extended survival, and nearly prevents pulmonary metastasis. This subcellular pretargeted strategy offers a robust platform for precision mitochondrial drug delivery, enhancing therapeutic potential of various cytotoxic agents in cancer immunotherapy.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c12201
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c12201
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
