德国慕尼黑大学Schtz, Anne K.团队报道了AAA+蛋白p97在原子水平上表征ATP的加工过程。相关研究成果于2024年2月7日发表于国际一流学术期刊《自然—化学》。
人类酶p97通过以ATP依赖的方式展开数百种蛋白质底物来调节各种细胞途径,使其成为蛋白质稳态的重要组成部分和有影响力的药理学靶点。六聚体复合物在其整个催化循环中经历显著的构象变化。
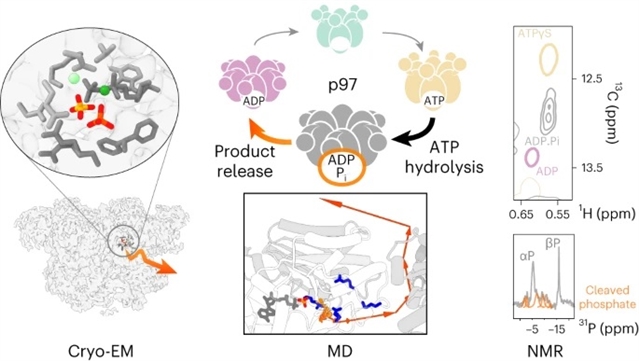
该文中,通过合并冷冻电镜、核磁共振波谱和分子动力学模拟,阐明了ATP水解前后时间窗口中活性位点发生的分子运动。p97存在一种亚稳态反应中间体,ADP·Pi态,它处于水解和产物释放之间。详细的快照显示,活性位点经过精细调整,可以捕获并最终释放裂解的磷酸盐。源自活性位点的信号通路协调六聚体亚基的作用,并将水解与变构构象变化耦合。
该多学科方法使人们得以一窥原型AAA+蛋白对ATP处理的复杂空间和时间协调。
附:英文原文
Title: Characterizing ATP processing by the AAA+ protein p97 at the atomic level
Author: Shein, Mikhail, Hitzenberger, Manuel, Cheng, Tat Cheung, Rout, Smruti R., Leitl, Kira D., Sato, Yusuke, Zacharias, Martin, Sakata, Eri, Schtz, Anne K.
Issue&Volume: 2024-02-07
Abstract: The human enzyme p97 regulates various cellular pathways by unfolding hundreds of protein substrates in an ATP-dependent manner, making it an essential component of protein homeostasis and an impactful pharmacological target. The hexameric complex undergoes substantial conformational changes throughout its catalytic cycle. Here we elucidate the molecular motions that occur at the active site in the temporal window immediately before and after ATP hydrolysis by merging cryo-EM, NMR spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations. p97 populates a metastable reaction intermediate, the ADP·Pi state, which is poised between hydrolysis and product release. Detailed snapshots reveal that the active site is finely tuned to trap and eventually discharge the cleaved phosphate. Signalling pathways originating at the active site coordinate the action of the hexamer subunits and couple hydrolysis with allosteric conformational changes. Our multidisciplinary approach enables a glimpse into the sophisticated spatial and temporal orchestration of ATP handling by a prototype AAA+ protein.
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-024-01440-0
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-024-01440-0
Nature Chemistry:《自然—化学》,创刊于2009年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:24.274
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nchem/
投稿链接:https://mts-nchem.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
