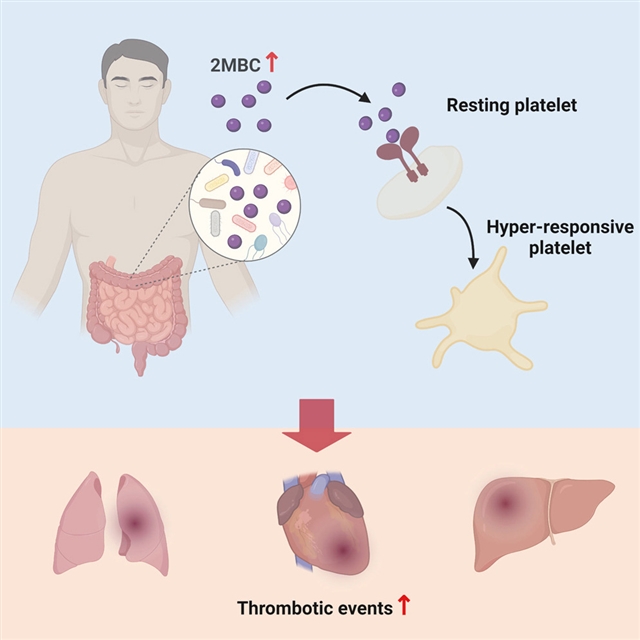
中山大学陈思凡等研究人员合作发现,肠道微生物代谢物2-甲基丁酰基肉碱通过结合并激活整合素α2β1使血栓形成加剧。相关论文于2024年2月23日在线发表在《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
研究人员表明,支链酰基肉碱——2-甲基丁酰基肉碱(2MBC)会在COVID-19患者和重大不良心血管事件(MACE)患者体内蓄积。2MBC可增强小鼠的血小板高反应性和血栓形成。从机理上讲,2MBC与血小板中的整合素α2β1结合,增强细胞膜磷脂酶A2(cPLA2)的活化和血小板的高反应性。基因耗竭或药物抑制整合素α2β1可在很大程度上逆转2MBC的促血栓形成作用。
值得注意的是,2MBC可以通过肠道微生物群依赖的方式产生,而血浆中2MBC的积累及其对血栓形成的促进作用在抗生素诱导的微生物耗竭后,会得到很大程度的改善。该研究表明,2MBC是一种代谢物,它将肠道微生物群失调与血栓风险升高联系在一起,为血栓形成提供了机理认识和潜在的治疗策略。
据悉,血栓形成是MACE导致死亡和残疾的主要原因。许多病理情况,如COVID-19和代谢紊乱,都会导致血栓风险增加;然而,人们对其潜在机制仍然知之甚少。
附:英文原文
Title: Gut microbial co-metabolite 2-methylbutyrylcarnitine exacerbates thrombosis via binding to and activating integrin α2β1
Author: Kan Huang, Zilun Li, Xi He, Jun Dai, Bingding Huang, Yongxia Shi, Dongxiao Fan, Zefeng Zhang, Yunchong Liu, Na Li, Zhongyu Zhang, Jiangyun Peng, Chenshu Liu, Renli Zeng, Zhipeng Cen, Tengyao Wang, Wenchao Yang, Meifeng Cen, Jingyu Li, Shuai Yuan, Lu Zhang, Dandan Hu, Shuxiang Huang, Pin Chen, Peilong Lai, Liyan Lin, Jielu Wen, Zhengde Zhao, Xiuyi Huang, Lining Yuan, Lifang Zhou, Haoliang Wu, Lihua Huang, Kai Feng, Jian Wang, Baolin Liao, Weiping Cai, Xilong Deng, Yueping Li, Jianping Li, Zhongwei Hu, Li Yang, Jiaojiao Li, Youguang Zhuo, Fuchun Zhang, Lin Lin, Yifeng Luo, Wei Zhang, Qianlin Ni, Xiqiang Hong, Guangqi Chang, Yang Zhang, Dongxian Guan, Weikang Cai, Yutong Lu, Fang Li, Li Yan, Meng Ren, Linghua Li, Sifan Chen
Issue&Volume: 2024-02-23
Abstract: Thrombosis represents the leading cause of death and disability upon major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs). Numerous pathological conditions such as COVID-19 andmetabolic disorders can lead to a heightened thrombotic risk; however, the underlyingmechanisms remain poorly understood. Our study illustrates that 2-methylbutyrylcarnitine(2MBC), a branched-chain acylcarnitine, is accumulated in patients with COVID-19 andin patients with MACEs. 2MBC enhances platelet hyperreactivity and thrombus formationin mice. Mechanistically, 2MBC binds to integrin α2β1 in platelets, potentiating cytosolicphospholipase A2 (cPLA2) activation and platelet hyperresponsiveness. Genetic depletionor pharmacological inhibition of integrin α2β1 largely reverses the pro-thromboticeffects of 2MBC. Notably, 2MBC can be generated in a gut-microbiota-dependent manner,whereas the accumulation of plasma 2MBC and its thrombosis-aggravating effect arelargely ameliorated following antibiotic-induced microbial depletion. Our study implicates2MBC as a metabolite that links gut microbiota dysbiosis to elevated thrombotic risk,providing mechanistic insight and a potential therapeutic strategy for thrombosis.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.01.014
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(24)00014-7
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
