美国华盛顿大学医学院Alex S. Holehouse团队近期取得重要工作进展,他们研究提出了从序列直接预测内在无序的蛋白质构象性质的方法。相关研究成果2024年1月31日在线发表于《自然—方法学》杂志上。
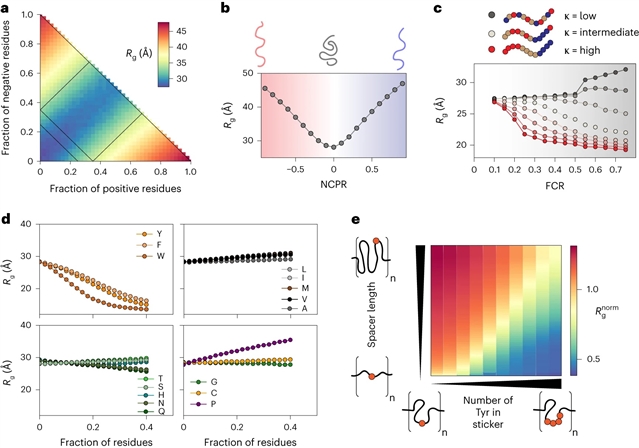
据介绍,内在无序区(IDR)普遍存在于生命的所有领域,并发挥着一系列功能作用。虽然折叠域通常用稳定的三维结构来很好地描述,但IDR存在于一组称为系综的相互转换状态中。这种结构异质性意味着IDR在很大程度上不存在于蛋白质数据库中,这导致缺乏从序列中预测整体构象特性的计算方法。
研究人员将合理的序列设计、大规模分子模拟和深度学习相结合,开发ALBATROS,这是一种深度学习模型,用于直接从蛋白质组范围的序列中预测IDR的集合维度,包括回转半径、端到端距离、聚合物标度指数和整体非球面度。ALBATROSS是轻量级的,易于使用,可作为本地安装的软件包和通过Google Colab笔记本电脑的点击式界面访问。研究人员首先通过检查IDR中序列-集合关系的可推广性来证明这一预测因子的适用性。然后,研究人员利用ALBATROSS的高通量特性,来表征蛋白质组内和蛋白质组间IDR的序列特异性生物物理行为。
附:英文原文
Title: Direct prediction of intrinsically disordered protein conformational properties from sequences
Author: Lotthammer, Jeffrey M., Ginell, Garrett M., Griffith, Daniel, Emenecker, Ryan J., Holehouse, Alex S.
Issue&Volume: 2024-01-31
Abstract: Intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) are ubiquitous across all domains of life and play a range of functional roles. While folded domains are generally well described by a stable three-dimensional structure, IDRs exist in a collection of interconverting states known as an ensemble. This structural heterogeneity means that IDRs are largely absent from the Protein Data Bank, contributing to a lack of computational approaches to predict ensemble conformational properties from sequence. Here we combine rational sequence design, large-scale molecular simulations and deep learning to develop ALBATROSS, a deep-learning model for predicting ensemble dimensions of IDRs, including the radius of gyration, end-to-end distance, polymer-scaling exponent and ensemble asphericity, directly from sequences at a proteome-wide scale. ALBATROSS is lightweight, easy to use and accessible as both a locally installable software package and a point-and-click-style interface via Google Colab notebooks. We first demonstrate the applicability of our predictors by examining the generalizability of sequence–ensemble relationships in IDRs. Then, we leverage the high-throughput nature of ALBATROSS to characterize the sequence-specific biophysical behavior of IDRs within and between proteomes.
DOI: 10.1038/s41592-023-02159-5
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-023-02159-5
Nature Methods:《自然—方法学》,创刊于2004年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:47.99
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nmeth/
投稿链接:https://mts-nmeth.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
