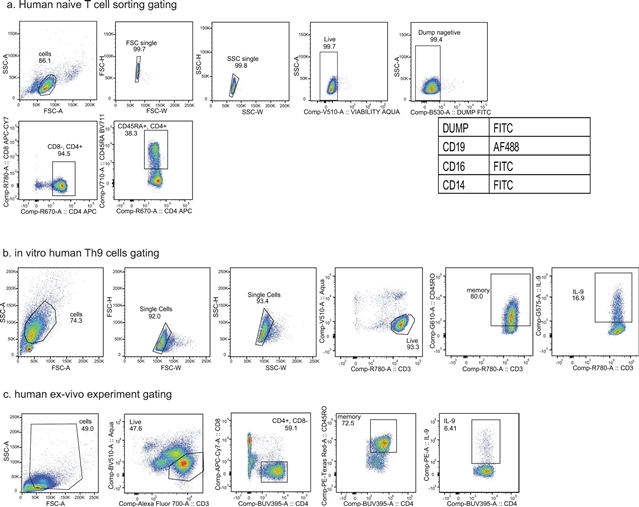
美国国立卫生研究院Daniella M. Schwartz研究组取得一项新突破。他们的研究发现在辅助性T9(TH9)细胞中,染色质动态可及性诱导STAT5和STAT6依赖性先天免疫功能以促进过敏性炎症。这一研究成果发表在2023年4月27日出版的国际学术期刊《自然—免疫学》上。
研究人员发现静息的TH9细胞由STAT5和STAT6依赖的旁观者通路激活,而独立于T细胞受体(TCR)再刺激产生白细胞介素(IL)-9。这种机制在过敏患者的循环细胞中可见,并且仅限于最近激活的细胞。依赖于STAT5的Il9/IL9调节元件随着时间的推移发生重塑使位点失活。更广泛的“过敏TH9”转录组学和表观基因组学基序也不稳定。在体内,TH9细胞通过TCR非依赖性、STAT依赖性机制诱导气道炎症。在过敏患者中,TH9细胞扩增与对JAK抑制剂的反应有关。
这些发现表明,TH9细胞的不稳定性是旁观者激活的阴性检查点并在过敏发生时分解,对于TH9细胞扩增的过敏患者,应考虑使用JAK抑制剂治疗。
研究人员表示,过敏性疾病是威胁人类健康的常见问题之一。产生IL-9的TH9细胞促进过敏性炎症,但尚不完全清楚TH9效应细胞的功能,其谱系不稳定性使其难以被研究。
附:英文原文
Title: Dynamic chromatin accessibility licenses STAT5- and STAT6-dependent innate-like function of TH9 cells to promote allergic inflammation
Author: Son, Aran, Meylan, Francoise, Gomez-Rodriguez, Julio, Kaul, Zenia, Sylvester, McKella, Falduto, Guido H., Vazquez, Estefania, Haque, Tamara, Kitakule, Moses M., Wang, Chujun, Manthiram, Kalpana, Qi, Chen-Feng, Cheng, Jun, Gurram, Rama K., Zhu, Jinfang, Schwartzberg, Pamela, Milner, Joshua D., Frischmeyer-Guerrerio, Pamela A., Schwartz, Daniella M.
Issue&Volume: 2023-04-27
Abstract: Allergic diseases are a major global health issue. Interleukin (IL)-9-producing helper T (TH9) cells promote allergic inflammation, yet TH9 cell effector functions are incompletely understood because their lineage instability makes them challenging to study. Here we found that resting TH9 cells produced IL-9 independently of T cell receptor (TCR) restimulation, due to STAT5- and STAT6-dependent bystander activation. This mechanism was seen in circulating cells from allergic patients and was restricted to recently activated cells. STAT5-dependent Il9/IL9 regulatory elements underwent remodeling over time, inactivating the locus. A broader ‘allergic TH9’ transcriptomic and epigenomic program was also unstable. In vivo, TH9 cells induced airway inflammation via TCR-independent, STAT-dependent mechanisms. In allergic patients, TH9 cell expansion was associated with responsiveness to JAK inhibitors. These findings suggest that TH9 cell instability is a negative checkpoint on bystander activation that breaks down in allergy and that JAK inhibitors should be considered for allergic patients with TH9 cell expansion.
DOI: 10.1038/s41590-023-01501-5
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41590-023-01501-5
Nature Immunology:《自然—免疫学》,创刊于2000年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:31.25
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/ni/
投稿链接:https://mts-ni.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
