近日,意大利Sistemi Complessi研究所的Mattia Scandolo课题组取得一项新成果。经过不懈努力,他们发现了3.99维自然蜂群。相关研究成果已于2023年4月24日在国际知名学术期刊《自然—物理学》上发表。
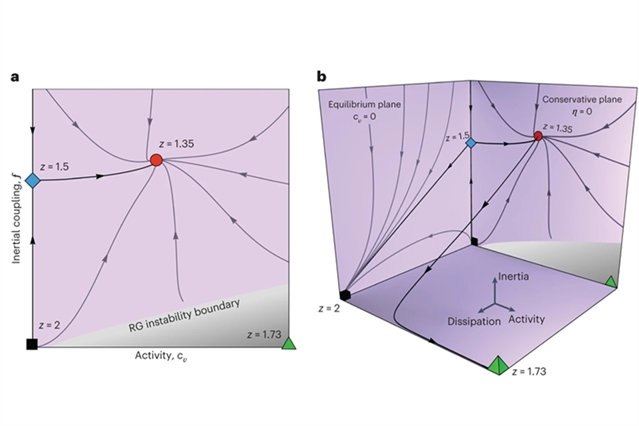
该研究团队利用4d阶重整化群方法计算了自然昆虫群体的动态临界指数z,这是将重整化群的预测能力扩展到集体生物系统方向迈出的重要一步。研究人员报道了一个新的固定点的出现,其中活动度和惯性都是相关的。在三维中,新固定点的临界指数为z=1.35,与实验(1.37±0.11)和数值模拟(1.35±0.04)一致。该研究结果深入探讨了重整化群对集体行为的定量描述能力,并暗示普适性在强相关生物系统中可能起到决定性作用。
据悉,重整化群是统计物理学中的一个重要概念和量化工具,可用于计算不同种类集体系统行为的普适量。如果能将重整化群的预测能力扩展到集体生物系统中,将极大地加强将物理学和生物学相结合的努力。
附:英文原文
Title: Natural swarms in 3.99 dimensions
Author: Cavagna, Andrea, Di Carlo, Luca, Giardina, Irene, Grigera, Toms S., Melillo, Stefania, Parisi, Leonardo, Pisegna, Giulia, Scandolo, Mattia
Issue&Volume: 2023-04-24
Abstract: The renormalization group is a key set of ideas and quantitative tools of statistical physics that allow for the calculation of universal quantities that encompass the behaviour of different kinds of collective systems. Extension of the predictive power of the renormalization group to collective biological systems would greatly strengthen the effort to put physical biology on a firm basis. Here we present a step in that direction by calculating the dynamical critical exponent z of natural swarms of insects using the renormalization group to order =4d. We report the emergence of a novel fixed point, where both activity and inertia are relevant. In three dimensions, the critical exponent at the new fixed point is z=1.35, in agreement with both experiments (1.37±0.11) and numerical simulations (1.35±0.04). Our results probe the power of the renormalization group for the quantitative description of collective behaviour, and suggest that universality may also play a decisive role in strongly correlated biological systems.
DOI: 10.1038/s41567-023-02028-0
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-023-02028-0
