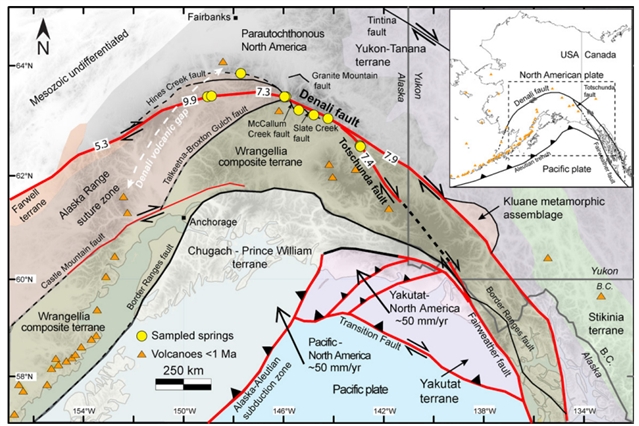
美国犹他州州立大学Dennis L. Newell小组报道了通过阿拉斯加德纳里断层岩石圈尺度的地幔-地表挥发性通量。该项研究成果发表在2023年4月13日出版的《地质学》上。
研究显示,位于2002年7.9级德纳里断层,地震破裂以西的主链上的温泉的3He / 4He 高达2.4 RC / RA (空气校正3He / 4He相对于空气的比率),表明地幔He含量约为 30%。相应的δ13C值为-9.1‰到-7.8‰(相当于Vienna Peedee箭石),表明这些西部泉的二氧化碳部分来自地幔。在2002年底破裂的东端,Totschunda断层泉有0.65-0.99 RC / RA (约 8%- 12%的地幔He)的3He / 4He,和来自碳酸盐的δ13C值(约 0‰)。
结果证实德纳里断层系统具有利用地幔挥发物的岩石圈尺度的特征。沿着2002年断裂的泉水产生了类似空气的3He / 4He,其比值为1 R / RA和 δ13C值为-9.2‰ 到-3.4‰,被解释为没有地幔作用影响,且代表了通过页岩、碳酸盐的浅层地下水循环。
平行与断裂带的逆冲展曲具有类似空气的3He / 4He,而沿走向的高角度正常展曲产生了1.3 RC / RA 的3He / 4He(地幔He含量约为16%),这意味着沿着断裂带的流动路径在断层带的上部10km处被中断。因为德纳里断层是一个岩石圈规模的,横贯北美和独立运动的阿拉斯加南部的构造,研究人员认为它具有转换边界的特征。研究结果与相似构造环境下氦同位素值的相似性表明,在没有岩浆作用影响的情况下,通过大陆走滑断层的地幔流体流量最大。
据研究人员介绍,沿德纳里断层系统(美国阿拉斯加州)400km区段的12个泉的氦和碳同位素数据,揭示了这一神秘结构的地幔-地表联系。
附:英文原文
Title: Roadblocks and speed limits: Mantle-to-surface volatile flux through the lithospheric-scale Denali fault, Alaska
Author: Dennis L. Newell, Jeff A. Benowitz, Sean P. Regan, Coleman D. Hiett
Issue&Volume: 2023-04-13
Abstract: Helium and carbon isotopic data from 12 springs along a ~400 km segment of the Denali fault system (Alaska, USA), inform mantle-to-surface connections of this enigmatic structure. Warm springs on the main strand, west of the 2002 M7.9 Denali fault earthquake rupture, have 3He / 4He as high as 2.4 RC / RA (air-corrected 3He / 4He relative to air ratio) indicating ~30% mantle He. Corresponding δ13C values are -9.1‰ to -7.8‰ (relative to Vienna Peedee belemnite), suggesting that the CO2 at these western springs is partially mantle derived. At the eastern end of the 2002 rupture, Totschunda fault springs have 3He / 4He of 0.650.99 RC / RA (~8%-12% mantle He), with δ13C values (~0‰) from carbonates. Results confirm the Denali fault system is a lithospheric-scale feature tapping mantle volatiles. Springs along the 2002 rupture yield air-like 3He / 4He of 1 R / RA and δ13C values from -9.2‰ to -3.4‰, interpreted as representing shallow groundwater circulation through shales and carbonates without mantle contributions. A thrust splay parallel to the rupture zone has air-like 3He / 4He, whereas an along-strike high-angle normal splay yields 3He / 4He of 1.3 RC / RA (~16% mantle He), implying that flow paths along the ruptured strand are disrupted in the upper 10 km of the fault zone. Because the Denali fault is a lithospheric-scale, transcurrent structure separating North America from independently moving southern Alaska, we suggest that it has characteristics of a transform boundary. The similarity of our results to helium isotope values at analogous tectonic settings suggest that without magmatism influence, there is a maximum mantle fluid flux through continental strike-slip faults.
DOI: 10.1130/G51068.1
Geology:《地质学》,创刊于1973年。隶属于美国地质学会,最新IF:6.324
官方网址:https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/geology
投稿链接:https://geology.msubmit.net/cgi-bin/main.plex
