德国马克斯普朗克代谢研究所Henning Fenselau等研究人员合作发现下丘脑中恢复体重的一个饥饿感突触放大器。相关论文于2023年3月24日在线发表在《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
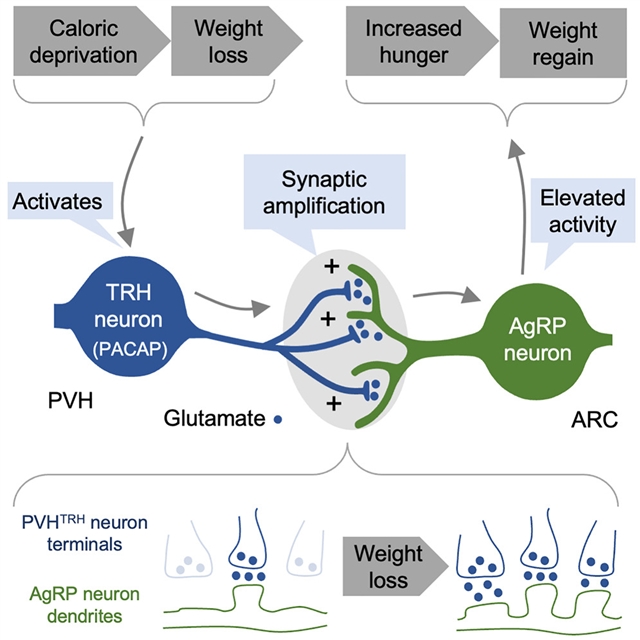
研究人员探究了促进饥饿的AgRP神经元上离散兴奋传入的突触可塑性的贡献。研究人员揭示了源自室旁下丘脑促甲状腺素释放(PVHTRH)神经元的活动依赖性、明显持久的突触活动放大在长期体重控制中的关键作用。沉默PVHTRH神经元可抑制对AgRP神经元兴奋性输入的增效,并减少随之而来的体重恢复。对该通路的短暂刺激足以持久地增强这种谷氨酸饥饿突触,并引发NMDAR依赖性的体重增加,且这种情况持久地持续下去。这种活动依赖的突触放大器的鉴定提供了一个以前未被认识到的靶点,用于对抗体重的恢复。
据介绍,限制热量摄入能有效地降低体重,但大多数节食者不能长期坚持热量不足,最终会重新获得失去的体重。控制饥饿感的下丘脑回路在很大程度上决定了体重;然而,减肥如何雕刻这些回路来激励食物消费,直到失去的体重被重新获得,仍然不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: A synaptic amplifier of hunger for regaining body weight in the hypothalamus
Author: Katarzyna Grzelka, Hannah Wilhelms, Stephan Dodt, Marie-Luise Dreisow, Joseph C. Madara, Samuel J. Walker, Chen Wu, Daqing Wang, Bradford B. Lowell, Henning Fenselau
Issue&Volume: 2023-03-24
Abstract: Restricting caloric intake effectively reduces body weight, but most dieters fail long-term adherence to caloric deficit and eventually regain lost weight. Hypothalamic circuits that control hunger drive critically determine body weight; yet, how weight loss sculpts these circuits to motivate food consumption until lost weight is regained remains unclear. Here, we probe the contribution of synaptic plasticity in discrete excitatory afferents on hunger-promoting AgRP neurons. We reveal a crucial role for activity-dependent, remarkably long-lasting amplification of synaptic activity originating from paraventricular hypothalamus thyrotropin-releasing (PVHTRH) neurons in long-term body weight control. Silencing PVHTRH neurons inhibits the potentiation of excitatory input to AgRP neurons and diminishes concomitant regain of lost weight. Brief stimulation of the pathway is sufficient to enduringly potentiate this glutamatergic hunger synapse and triggers an NMDAR-dependent gaining of body weight that enduringly persists. Identification of this activity-dependent synaptic amplifier provides a previously unrecognized target to combat regain of lost weight.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.03.002
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(23)00080-3
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
