美国现代饮食与生理研究中心Dana M. Small和德国马克斯普朗克代谢研究所Marc Tittgemeyer共同合作,近期取得重要工作进展。他们研究发现人类每天习惯性摄入甜食和高脂肪零食会调节奖赏过程。相关研究成果2023年3月22日在线发表于《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
据介绍,富含脂肪和糖的西方饮食会促进热量摄入过多和体重增加,然而,其潜在机制目前尚不清楚。尽管有充分的证据表明肥胖与大脑多巴胺功能改变之间存在联系,但这些改变是否是(1)预先存在的,增加了个体对体重增加的易感性,(2)继发于肥胖,或(3)直接归因于反复接触西方饮食,目前尚不清楚。
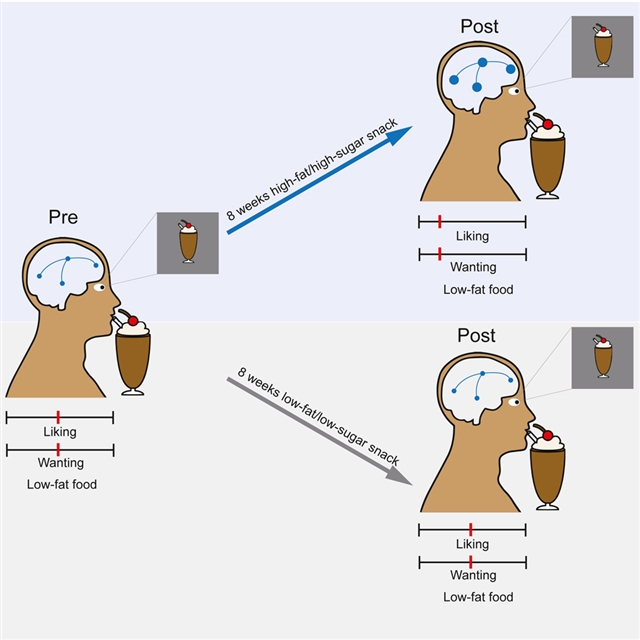
为了缩小这一差距,研究人员对正常体重的参与者进行了一项随机对照研究(NCT05574660),除了常规饮食外,他们还接触了连续8周的高脂肪/高糖零食或低脂/低糖零食。高脂肪/高糖干预降低了对低脂食物的偏好,同时增加了大脑对食物的反应和独立于食物线索或奖励的联想学习。
总之,这些变化与体重和代谢参数的变化无关,表明高脂肪、高糖食物对神经行为适应的直接影响可能会增加暴饮暴食和体重增加的风险。
附:英文原文
Title: Habitual daily intake of a sweet and fatty snack modulates reward processing in humans
Author: Sharmili Edwin Thanarajah, Alexandra G. DiFeliceantonio, Kerstin Albus, Bojana Kuzmanovic, Lionel Rigoux, Sandra Iglesias, Ruth Hanen, Marc Schlamann, Oliver A. Cornely, Jens C. Brüning, Marc Tittgemeyer, Dana M. Small
Issue&Volume: 2023-03-22
Abstract: Western diets rich in fat and sugar promote excess calorie intake and weight gain; however, the underlying mechanisms are unclear. Despite a well-documented association between obesity and altered brain dopamine function, it remains elusive whether these alterations are (1) pre-existing, increasing the individual susceptibility to weight gain, (2) secondary to obesity, or (3) directly attributable to repeated exposure to western diet. To close this gap, we performed a randomized, controlled study (NCT05574660) with normal-weight participants exposed to a high-fat/high-sugar snack or a low-fat/low-sugar snack for 8 weeks in addition to their regular diet. The high-fat/high-sugar intervention decreased the preference for low-fat food while increasing brain response to food and associative learning independent of food cues or reward. These alterations were independent of changes in body weight and metabolic parameters, indicating a direct effect of high-fat, high-sugar foods on neurobehavioral adaptations that may increase the risk for overeating and weight gain.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.02.015
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(23)00051-7
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
