近日,美国加州大学的Yao, N. Y&A. C. Bleszynski课题组与哈佛大学的D.Bluvstein合作,探究了二维偶极自旋系综中的多体动力学。相关研究成果已于2023年3月16日在国际权威学术期刊《自然—物理学》上发表。
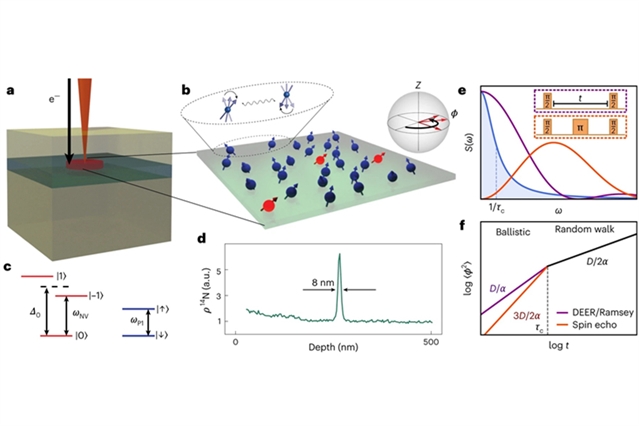
该课题组使用探针的退相干动力学来获得有关多体系统的信息。研究人员利用可光学寻址的探针自旋来实验性地表征强相互作用磁偶极体系的静态和动态性质。他们的实验平台由氮δ掺杂金刚石中的两种自旋缺陷组成:氮-空位色心,将其用作探针自旋,以及替换氮杂质的多体系综。他们证明了多体系统的维数、动力学和无序性可以自然地编码在探针自旋的退相干特性中。此外,他们还直接控制了多体系统的光谱特性,具有量子传感和模拟中的潜在应用。
据悉,表征强相互作用系统的量子动力学最直接的方法是测量其完整多体状态的时间演化。尽管这种方法在概念上很简单,但随着系统规模的增长,它很快就变得难以处理。另一种方法是将多体动力学视为产生噪声,可以通过探针量子比特的退相干来测量。
附:英文原文
Title: Probing many-body dynamics in a two-dimensional dipolar spin ensemble
Author: Davis, E. J., Ye, B., Machado, F., Meynell, S. A., Wu, W., Mittiga, T., Schenken, W., Joos, M., Kobrin, B., Lyu, Y., Wang, Z., Bluvstein, D., Choi, S., Zu, C., Jayich, A. C. Bleszynski, Yao, N. Y.
Issue&Volume: 2023-03-16
Abstract: The most direct approach for characterizing the quantum dynamics of a strongly interacting system is to measure the time evolution of its full many-body state. Despite the conceptual simplicity of this approach, it quickly becomes intractable as the system size grows. An alternate approach is to think of the many-body dynamics as generating noise, which can be measured by the decoherence of a probe qubit. Here we investigate what the decoherence dynamics of such a probe tells us about the many-body system. In particular, we utilize optically addressable probe spins to experimentally characterize both static and dynamical properties of strongly interacting magnetic dipoles. Our experimental platform consists of two types of spin defects in nitrogen delta-doped diamond: nitrogen-vacancy colour centres, which we use as probe spins, and a many-body ensemble of substitutional nitrogen impurities. We demonstrate that the many-body system’s dimensionality, dynamics and disorder are naturally encoded in the probe spins’ decoherence profile. Furthermore, we obtain direct control over the spectral properties of the many-body system, with potential applications in quantum sensing and simulation.
DOI: 10.1038/s41567-023-01944-5
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-023-01944-5
