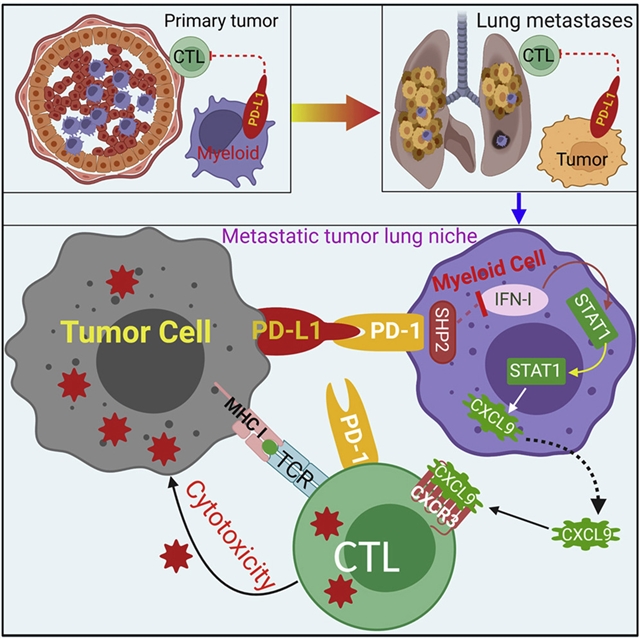
美国乔治亚癌症中心Kebin Liu研究团队发现肿瘤细胞PD-L1 (tPD-L1)利用髓系PD-1抑制I型干扰素,损害细胞毒性T淋巴细胞的募集。相关论文于2023年3月13日发表在《癌细胞》杂志上。
他们报道tPD-L1在肿瘤细胞和肿瘤特异性CTL共培养中不抑制细胞毒性T淋巴细胞(CTL)活性,对原发肿瘤生长无影响。然而,在荷瘤小鼠中,敲除tPD-L1以CTL依赖的方式减少肺转移。髓系细胞衰竭或敲除髓系细胞中的PD-1 (mPD-1)会损害tPD-L1促进小鼠肿瘤肺转移的作用。单细胞RNA测序(scRNA-seq)显示tPD-L1参与mPD-1激活SHP2拮抗I型干扰素(IFN-I)和STAT1通路抑制Cxcl9并损害肺转移的CTL募集。人类癌症患者对PD-1阻断免疫治疗的反应与髓细胞中的IFN-I反应相关。
他们的研究结果确定tPD-L1参与mPD-1激活SHP2抑制IFN-I-STAT1-CXCL9通路,从而损害肺转移中的CTL肿瘤募集。
据悉,tPD-L1在肿瘤免疫逃避中的作用的细胞和分子机制尚不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: Tumor PD-L1 engages myeloid PD-1 to suppress type I interferon to impair cytotoxic T lymphocyte recruitment
Author: John D. Klement, Priscilla S. Redd, Chunwan Lu, Alyssa D. Merting, Dakota B. Poschel, Dafeng Yang, Natasha M. Savage, Gang Zhou, David H. Munn, Padraic G. Fallon, Kebin Liu
Issue&Volume: 2023/03/13
Abstract: The cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying tumor cell PD-L1 (tPD-L1) function in tumor immune evasion are incompletely understood. We report here that tPD-L1 does not suppress cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) activity in co-cultures of tumor cells and tumor-specific CTLs and exhibits no effect on primary tumor growth. However, deleting tPD-L1 decreases lung metastasis in a CTL-dependent manner in tumor-bearing mice. Depletion of myeloid cells or knocking out PD-1 in myeloid cells (mPD-1) impairs tPD-L1 promotion of tumor lung metastasis in mice. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) reveals that tPD-L1 engages mPD-1 to activate SHP2 to antagonize the type I interferon (IFN-I) and STAT1 pathway to repress Cxcl9 and impair CTL recruitment to lung metastases. Human cancer patient response to PD-1 blockade immunotherapy correlates with IFN-I response in myeloid cells. Our findings determine that tPD-L1 engages mPD-1 to activate SHP2 to suppress the IFN-I-STAT1-CXCL9 pathway to impair CTL tumor recruitment in lung metastasis.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.02.005
Source: https://www.cell.com/cancer-cell/fulltext/S1535-6108(23)00033-8
Cancer Cell:《癌细胞》,创刊于2002年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:38.585
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cancer-cell/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cancer-cell/default.aspx
