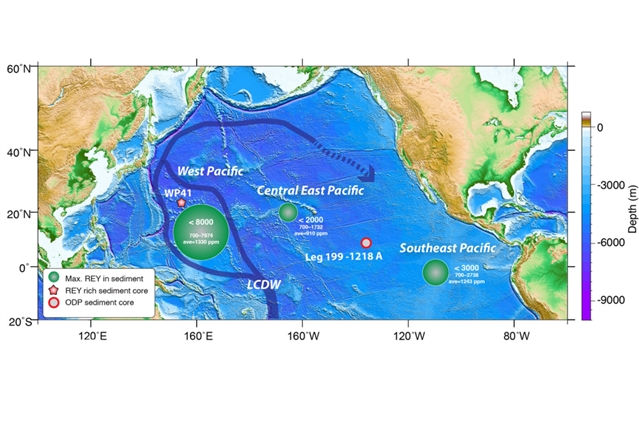
课题组人员报告了一个来自海洋钻探项目(199段,1218A孔)的岩芯和一个太平洋富含钇的沉积岩芯的生物磷灰石U-Pb年龄,分别为22.8到18.2 Ma和6.5到2.2 Ma。从1218A岩心获得的U-Pb鱼齿年龄符合生物地层的限制,为U-Pb生物磷灰石计时仪的应用提供了一个绝对的地层时间尺度,特别是在方解石补偿深度(CCD)以下的沉积层序。通过对富钇的沉积岩芯中富钇鱼齿的U-Pb年龄测定,表明西太平洋的成矿作用不晚于中新世。铀与钇呈正相关,表明铀和钇同时加入到鱼齿晶格中,使得生物磷灰石U- pb计时仪适用于约束钇成矿的时间。结合已发表的数据,研究表明,西太平洋中新世钇的堆积事件受到与缺氧底水相关的高P2O5和MnO2含量的影响。
据介绍,富含稀土元素和钇(REY)的深海沉积物是有前途的矿产资源,通常被认为与鱼类残骸的埋藏有关。然而,人们对钇富集的性质知之甚少,部分原因是缺乏强有力的年龄限制。
附:英文原文
Title: Dating rare earth element enrichment in deep-sea sediments using U-Pb geochronology of bioapatite
Author: Dengfeng Li, Jinzhou Peng, David Chew, Yongjia Liang, Pete Hollings, Yu Fu, Yanhui Dong, Xiaoming Sun
Issue&Volume: 2023-03-09
Abstract: Deep-sea sediments rich in rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) are promising mineral resources that are believed to be associated with the burial of fish debris. However, the nature of the REY enrichment is poorly understood, in part due to a lack of robust age constraints. We report bioapatite U-Pb ages from an Ocean Drilling Program (Leg 199, Hole 1218A) core and a REY-rich sedimentary core from the Pacific Ocean, which yielded U-Pb ages ranging from 22.8 to 18.2 Ma and 6.5 to 2.2 Ma, respectively. The U-Pb fish teeth ages from the 1218A core are consistent with biostratigraphic constraints, shed light on the application of the U-Pb bioapatite chronometer, and yield an absolute time scale for stratigraphy, especially for sequences deposited below the calcite compensation depth (CCD), where there is an absence of fossil carbonate. The successful measurement of U-Pb ages from REY-enriched fish teeth in the REY-rich sediment core suggests the mineralization occurred no later than the Miocene in the western Pacific Ocean. Uranium is positively correlated with REY, suggesting that the U and REY were incorporated into the fish teeth lattice simultaneously, making the bioapatite U-Pb chronometer suitable for constraining the timing of REY mineralization. When combined with published data, our study suggests that the Miocene REY accumulation event in the western Pacific Ocean was influenced by high P2O5 and MnO2 contents correlated with oxic bottom water.
DOI: 10.1130/G50938.1
Geology:《地质学》,创刊于1973年。隶属于美国地质学会,最新IF:6.324
官方网址:https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/geology
投稿链接:https://geology.msubmit.net/cgi-bin/main.plex
