近日,四川大学邵振华等研究人员合作揭示补体受体C5aR1激活和偏向信号的机制。2023年2月17日,《细胞研究》杂志在线发表了这项成果。
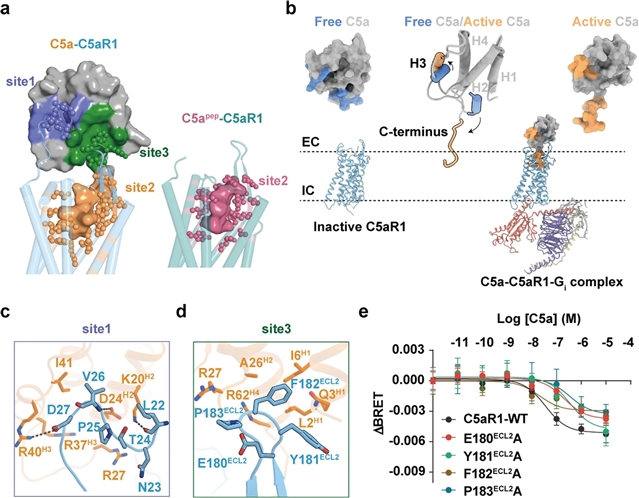
研究人员报道了活化的野生型C5a受体1(C5aR1)-Gi蛋白复合物的冷冻电子显微镜结构,该复合物与以下每种蛋白结合:C5a、六肽激动剂C5apep和G蛋白偏向激动剂BM213。这些结构揭示了C5a-C5aR1相互作用的格局,以及识别不同形位配体的共同模体。此外,结合诱变研究和基于细胞的药理学分析,研究人员通过破解C089诱导的C5aR1I116A突变体-Gi信号激活复合物(C5aR1对野生型C5aR1具有拮抗作用)的结构,破译了不同肽类似物偏向信号模体的框架,并对C5aR1的激活机制提供了深入的了解。此外,激动剂结合后,跨膜结构域7和螺旋8的胞内端发生了不一致的构象变化,提示信号转导过程存在差异。总的来说,这项研究为C5aR1的配体识别、偏向信号调节、激活和Gi蛋白偶联提供了机制理解,这可能有助于未来治疗剂的设计。
据介绍,补体系统在对入侵病原体的先天免疫反应中起着重要作用。补体片段C5a是其重要的效应成分之一,通过激活C5aR1及其下游G蛋白和β-抑制素信号通路发挥多种生理功能。C5a-C5aR1轴的功能障碍与许多炎症和免疫介导的疾病有关,但C5aR1激活和偏倚信号的结构基础仍不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: Mechanism of activation and biased signaling in complement receptor C5aR1
Author: Feng, Yuying, Zhao, Chang, Deng, Yue, Wang, Heli, Ma, Liang, Liu, Sicen, Tian, Xiaowen, Wang, Bo, Bin, Yan, Chen, Peipei, Yan, Wei, Fu, Ping, Shao, Zhenhua
Issue&Volume: 2023-02-17
Abstract: The complement system plays an important role in the innate immune response to invading pathogens. The complement fragment C5a is one of its important effector components and exerts diverse physiological functions through activation of the C5a receptor 1 (C5aR1) and associated downstream G protein and β-arrestin signaling pathways. Dysfunction of the C5a-C5aR1 axis is linked to numerous inflammatory and immune-mediated diseases, but the structural basis for activation and biased signaling of C5aR1 remains elusive. Here, we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of the activated wild-type C5aR1–Gi protein complex bound to each of the following: C5a, the hexapeptidic agonist C5apep, and the G protein-biased agonist BM213. The structures reveal the landscape of the C5a–C5aR1 interaction as well as a common motif for the recognition of diverse orthosteric ligands. Moreover, combined with mutagenesis studies and cell-based pharmacological assays, we deciphered a framework for biased signaling using different peptide analogs and provided insight into the activation mechanism of C5aR1 by solving the structure of C5aR1I116A mutant–Gi signaling activation complex induced by C089, which exerts antagonism on wild-type C5aR1. In addition, unusual conformational changes in the intracellular end of transmembrane domain 7 and helix 8 upon agonist binding suggest a differential signal transduction process. Collectively, our study provides mechanistic understanding into the ligand recognition, biased signaling modulation, activation, and Gi protein coupling of C5aR1, which may facilitate the future design of therapeutic agents.
DOI: 10.1038/s41422-023-00779-2
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41422-023-00779-2
Cell Research:《细胞研究》,创刊于1990年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:20.057
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/cr/
投稿链接:https://mts-cr.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
