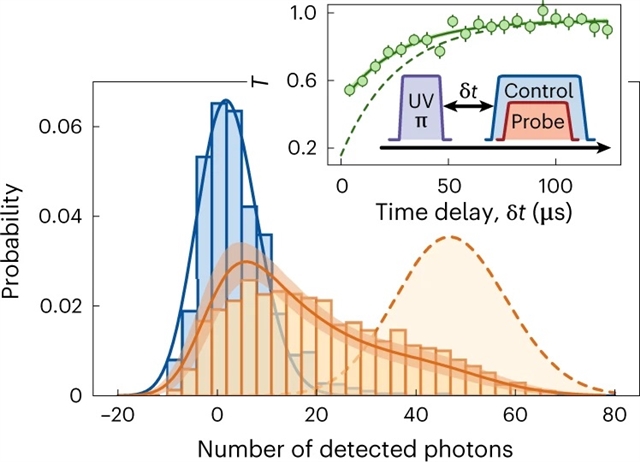
德国马克斯普朗克量子光学研究所的Johannes Zeiher课题组在研究中取得进展。他们研制了由单个里德伯格原子转化的亚波长原子阵列。2023年2月16日,国际知名学术期刊《自然—物理学》发表了这一成果。
研究团队通过实验证明对原子薄镜子光学响应的空间控制,这种原子薄镜子是由使用单独受控制的辅助原子激发到里德伯格态后形成的。通过在原子镜中加入少量的里德伯分数,实现了对转化行为的控制,并与附属原子产生了强烈的偶极里德伯格相互作用。研究团队在附属原子上驱动拉比振荡并证明了阵列传输和反射的相干控制。相关研究结果表明人类向量子相干超表面的实现以及受控原子-光子纠缠的演示和光量子态的确定性工程迈出重要一步。
据了解,在单量子水平上增强光物质耦合对量子科学的广泛应用至关重要。亚波长原子阵列的协同光响应被发现为这种强的光-物质耦合开辟了新的途径,同时提供了对光场多种空间模式的访问。虽然已报道过高效率的单模自由空间耦合到这样的阵列,但空间控制模式的出射光场仍然是不确定的。
附:英文原文
Title: A subwavelength atomic array switched by a single Rydberg atom
Author: Srakaew, Kritsana, Weckesser, Pascal, Hollerith, Simon, Wei, David, Adler, Daniel, Bloch, Immanuel, Zeiher, Johannes
Issue&Volume: 2023-02-16
Abstract: Enhancing light–matter coupling at the level of single quanta is essential for numerous applications in quantum science. The cooperative optical response of subwavelength atomic arrays has been found to open new pathways for such strong light–matter couplings, while simultaneously offering access to multiple spatial modes of the light field. Efficient single-mode free-space coupling to such arrays has been reported, but spatial control over the modes of outgoing light fields has remained elusive. Here, we demonstrate such spatial control over the optical response of an atomically thin mirror formed by a subwavelength array of atoms in free space using a single controlled ancilla atom excited to a Rydberg state. The switching behaviour is controlled by the admixture of a small Rydberg fraction to the atomic mirror, and consequently strong dipolar Rydberg interactions with the ancilla. Driving Rabi oscillations on the ancilla atom, we demonstrate coherent control of the transmission and reflection of the array. These results represent a step towards the realization of quantum coherent metasurfaces, the demonstration of controlled atom–photon entanglement and deterministic engineering of quantum states of light.
DOI: 10.1038/s41567-023-01959-y
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-023-01959-y
