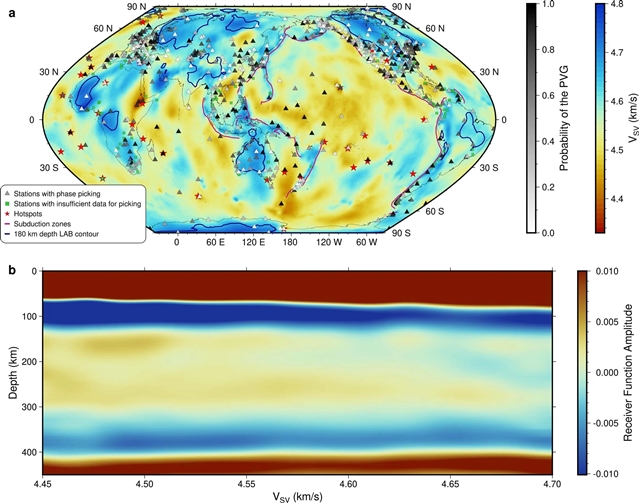
软流圈低速带与全球普遍存在的部分熔融相一致,这一成果由美国布朗大学Hua Junlin的研究组经过不懈努力而取得。相关论文于2023年2月6日发表在《自然—地球科学》杂志上。
研究团队分析了来自全球分布的地震台站的接收函数数据,以成像软流层低地震速度带的下游。该研究人员提供了全球广泛的证据,证明在大约150km是代表软流圈内一个特别低速区的底部。这种边界最常在上地幔温度升高的地区被探测到,最好的模型是部分熔融层的底部。边界的存在与表征地幔累积应变的径向地震各向异性无关,表明推测的部分熔融对软流圈的大尺度黏度没有实质性影响。研究结果表明,在软流圈内存在一个广泛的、部分熔融的区域,但低软流圈粘度主要是由压力和温度随深度的逐渐变化所控制的。
据悉,软流圈在今天的板块构造中起着重要作用,因为它的低粘度控制着下面地幔中的对流如何在上面的地球表面表达。对软流圈的起源的研究,包括部分融化在降低其粘度和促进变形方面的作用仍然不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: Asthenospheric low-velocity zone consistent with globally prevalent partial melting
Author: Hua, Junlin, Fischer, Karen M., Becker, Thorsten W., Gazel, Esteban, Hirth, Greg
Issue&Volume: 2023-02-06
Abstract: The asthenosphere plays a fundamental role in present-day plate tectonics as its low viscosity controls how convection in the mantle below it is expressed at the Earth’s surface above. The origin of the asthenosphere, including the role of partial melting in reducing its viscosity and facilitating deformation, remains unclear. Here we analysed receiver-function data from globally distributed seismic stations to image the lower reaches of the asthenospheric low-seismic-velocity zone. We present globally widespread evidence for a positive seismic-velocity gradient at depths of ~150km, which represents the base of a particularly low-velocity zone within the asthenosphere. This boundary is most commonly detected in regions with elevated upper-mantle temperatures and is best modelled as the base of a partially molten layer. The presence of the boundary showed no correlation with radial seismic anisotropy, which represents accumulated mantle strain, indicating that the inferred partial melt has no substantial effect on the large-scale viscosity of the asthenosphere. These results imply the presence of a globally extensive, partially molten zone embedded within the asthenosphere, but that low asthenospheric viscosity is controlled primarily by gradual pressure and temperature variations with depth.
DOI: 10.1038/s41561-022-01116-9
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41561-022-01116-9
