原文链接:http://t.cn/Ai9xOYMN
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/q7UKwIC7LXbjF1m22oQT9Q
我们为您整理了BMC旗下基因组学旗舰刊Genome Biology和Genome Medicine的最新内容供您阅览。
Genome Biology

点击此处,查看原文
CRISPR directed evolution of the spliceosome for resistance to splicing inhibitor
Haroon Butt等人开发了一款适用于植物的进化平台,利用该平台可以助力水稻中的剪接体蛋白的进化从而抵抗剪接抑制剂。该研究可以对作物的性能和适应性加以改善。
DOI:10.1186/s13059-019-1680-9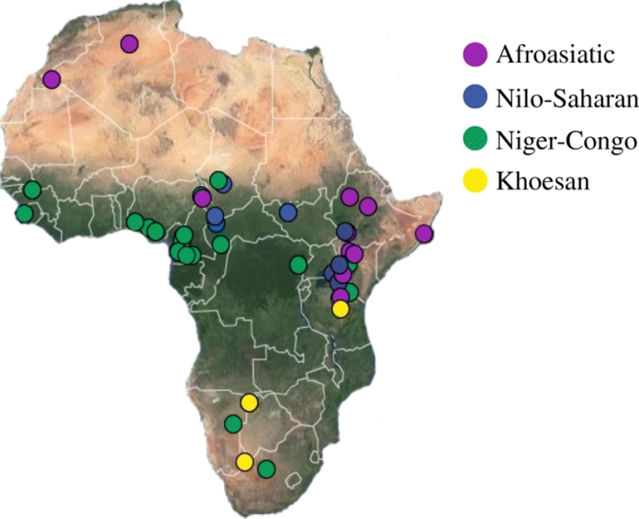
点击此处,查看原文
African evolutionary history inferred from whole genome sequence data of 44 indigenous African populations
来自复旦大学的Shaohua Fan和美国的研究人员发现44个非洲土著人群中有92个个体的高水平基因组变异与地理和语言相关。
DOI:10.1186/s13059-019-1679-2
其他文章
Genome-wide nucleotide patterns and potential mechanisms of genome divergence following domestication in maize and soybean
玉米和大豆驯化后的全基因组核苷酸模式及可能的基因组分化机制
Jinyu Wang et al.
DOI:10.1186/s13059-019-1683-6
Translation of the circular RNA circβ-catenin promotes liver cancer cell growth through activation of the Wnt pathway
环状RNA环β-连环蛋白的翻译通过激活Wnt通路促进肝癌细胞生长
Wei-Cheng Liang et al.
DOI:10.1186/s13059-019-1685-4
Plant lamin-like proteins mediate chromatin tethering at the nuclear periphery
植物核纤层蛋白介导核周边的染色质束缚
Bo Hu et al.
DOI:10.1186/s13059-019-1694-3
DegNorm: normalization of generalized transcript degradation improves accuracy in RNA-seq analysis
Degnorm:广义转录降解的标准化提高了RNA序列分析的准确性。
Bin Xiong et al
DOI:10.1186/s13059-019-1682-7
Measuring sequencer size bias using REcount: a novel method for highly accurate Illumina sequencing-based quantification
使用REcount测量测序仪检测结果的偏差:一种用于高度准确的基于Illumina测序的定量新方法
Daryl M. Gohl et al.
DOI:10.1186/s13059-019-1691-6
Bazam: a rapid method for read extraction and realignment of high-throughput sequencing data
Bazam:一种快速读取和重新排列高通量测序数据的方法
Simon P. Sadedin and Alicia Oshlack
DOI:10.1186/s13059-019-1688-1
Genome Medicine
合集征稿
“Clinical interpretation of genome variation”

点击此处,查看原文
Genome Medicine推出的该征稿合集重点关注对人类疾病(包括孟德尔病和复杂疾病以及罕见和常见疾病)的临床背景下基因组变异的了解。投稿截止日期是2019年9月。
亮点研究
点击此处,查看原文
Interchromosomal template-switching as a novel molecular mechanism for imprinting perturbations associated with Temple syndrome
染色体内三倍体(TRP)可通过基因剂量效应、基因的破坏、位置效应或基因的融合来促进疾病的成因。来自美国的Claudia M. B. Carvalho等人研究发现这种三倍体化可以导致节段性单亲二体化(UDP)和一些基因印记疾病。
DOI:10.1186/s13073-019-0633-y

点击此处,查看原文
Evidence from genome wide association studies implicates reduced control of Epstein-Barr virus infection in multiple sclerosis susceptibility
Ali Afrasiabi等人利用来自全基因组关联研究的结果证明了多发性硬化易感患者更易受到Epstein-Barr病毒的感染,该结果致力于提高对EBV参与多发性硬化症发展和新治疗靶点的理解。
DOI:10.1186/s13073-019-0640-z
其他文章
Multi-omics discovery of exome-derived neoantigens in hepatocellular carcinoma
肝细胞癌中外显子衍生的新抗原的多组学发现
Markus W. Löffler et al.
DOI:10.1186/s13073-019-0636-8
A modular transcriptome map of mature B cell lymphomas
成熟B细胞淋巴瘤的模块转录组图谱
Henry Loeffler-Wirth et al.
DOI:10.1186/s13073-019-0637-7
TCF21 and AP-1 interact through epigenetic modifications to regulate coronary artery disease gene expression
TCF21和AP-1通过表观遗传修饰相互作用来调节冠状动脉疾病基因表达
Quanyi Zhao et al.
DOI :10.1186/s13073-019-0635-9
CRISPR-SONIC: targeted somatic oncogene knock-in enables rapid in vivo cancer modeling
CRISPR-SONIC:靶向体细胞致癌基因敲入可实现快速体内癌症建模
Haiwei Mu et al.
DOI :10.1186/s13073-019-0627-9
阅读英文全文请访问:http://t.cn/Ai9xOYMN
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。