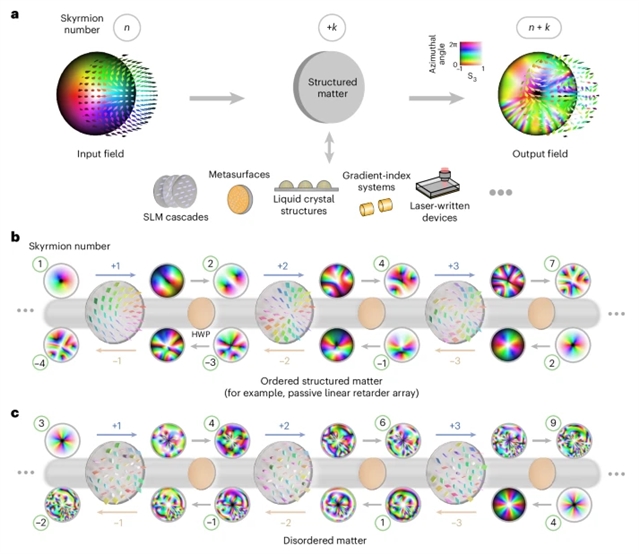
近日,英国牛津大学He, Chao团队研究了利用光学斯格明子的扰动弹性整数算法。2025年10月27日出版的《自然—光子学》杂志发表了这项成果。
摩尔定律的衰落加上人工智能的兴起,最近激发了对光子计算的研究,将其作为一种高带宽、低功耗的策略来加速数字电子技术的发展。然而,许多现代光子计算策略是模拟的,这使得它们容易受到噪声的影响,并且本质上难以扩展。光学斯格明子为克服这些限制提供了一条途径,通过数字化的形式,可以将离散拓扑数分配给模拟光学场。除了固有的抗扰动性外,光学斯格明子代表了一种尚未完全用于光子计算的新介质,即空间变化偏振。
研究组提出并实验证明了一种使用光学斯格明子和无源光学元件执行微扰弹性整数算法的方法,实现了在没有外部能量输入的情况下直接对光学斯格明子进行离散数学运算。
附:英文原文
Title: Perturbation-resilient integer arithmetic using optical skyrmions
Author: Wang, An Aloysius, Ma, Yifei, Zhang, Yunqi, Zhao, Zimo, Cai, Yuxi, Qiu, Xuke, Dong, Bowei, He, Chao
Issue&Volume: 2025-10-27
Abstract: The decline of Moore’s law coupled with the rise of artificial intelligence has recently motivated research into photonic computing as a high-bandwidth, low-power strategy to accelerate digital electronics. However, many modern-day photonic computing strategies are analogue, making them susceptible to noise and intrinsically difficult to scale. Optical skyrmions offer a route to overcome these limitations through digitization in the form of a discrete topological number that can be assigned to the analogue optical field. Apart from an intrinsic robustness against perturbations, optical skyrmions represent a new medium that has yet to be fully exploited for photonic computing, namely, spatially varying polarization. Here we propose and experimentally demonstrate a method for performing perturbation-resilient integer arithmetic with optical skyrmions and passive optical components, achieving discrete mathematical operations directly using optical skyrmions without external energy input.
DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01779-x
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-025-01779-x
