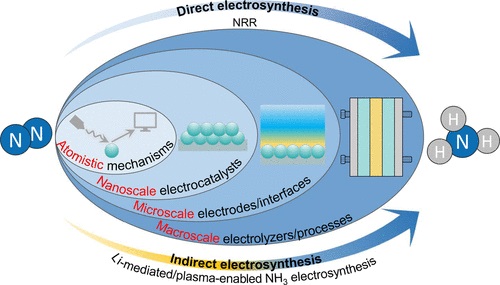
据了解,绿色氨(NH3)是利用可再生电力分解几乎无限量的氮(N2)分子而制成的一种重要的平台分子,是不排放二氧化碳、推动人类社会可持续发展的理想燃料。NH3电合成领域目前面临着产率低、效率低的困境。然而,解耦该领域的重叠问题并为其发展方向提供指导并非易事,因为它涉及复杂的反应过程和多学科(例如,电化学,催化,界面,过程等)。
从这个角度来看,研究人员介绍了一种基于反应过程的NH3电合成分类方案,即直接(N2还原反应)和间接电合成(Li介导/等离子体使能NH3电合)。这种分类使人们能够精细地解耦复杂的反应途径,并确定每种合成方法的具体速率决定步骤/瓶颈问题,如N2活化、析氢副反应、固体电解质界面工程、等离子体工艺等。然后,从电催化剂、电极、电解质、电解槽等电化学体系的角度详细综述了解决这些核心问题的最新进展。最后,从原子机制、纳米级电催化剂、微尺度电极/界面和宏观尺度电解槽/工艺等多个角度,展望了NH3电合成的研究方向和发展方向。
研究人员希望这篇文章能够为读者提供对瓶颈问题的深入理解,并为设计高效的NH3电合成体系提供有见地的指导。
附:英文原文
Title: NH3 Electrosynthesis from N2 Molecules: Progresses, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Author: Yongwen Ren, Shaofeng Li, Chang Yu, Yihan Zheng, Cheng Wang, Bingzhi Qian, Linshan Wang, Wenhui Fang, Ying Sun, Jieshan Qiu
Issue&Volume: February 27, 2024
Abstract: Green ammonia (NH3), made by using renewable electricity to split nearly limitless nitrogen (N2) molecules, is a vital platform molecule and an ideal fuel to drive the sustainable development of human society without carbon dioxide emission. The NH3 electrosynthesis field currently faces the dilemma of low yield rate and efficiency; however, decoupling the overlapping issues of this area and providing guidelines for its development directions are not trivial because it involves complex reaction process and multidisciplinary entries (for example, electrochemistry, catalysis, interfaces, processes, etc.). In this Perspective, we introduce a classification scheme for NH3 electrosynthesis based on the reaction process, namely, direct (N2 reduction reaction) and indirect electrosynthesis (Li-mediated/plasma-enabled NH3 electrosynthesis). This categorization allows us to finely decouple the complicated reaction pathways and identify the specific rate-determining steps/bottleneck issues for each synthesis approach such as N2 activation, H2 evolution side reaction, solid-electrolyte interphase engineering, plasma process, etc. We then present a detailed overview of the latest progresses on solving these core issues in terms of the whole electrochemical system covering the electrocatalysts, electrodes, electrolytes, electrolyzers, etc. Finally, we discuss the research focuses and the promising strategies for the development of NH3 electrosynthesis in the future with a multiscale perspective of atomistic mechanisms, nanoscale electrocatalysts, microscale electrodes/interfaces, and macroscale electrolyzers/processes. It is expected that this Perspective will provide the readers with an in-depth understanding of the bottleneck issues and insightful guidance on designing the efficient NH3 electrosynthesis systems.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c11676
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.3c11676
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
